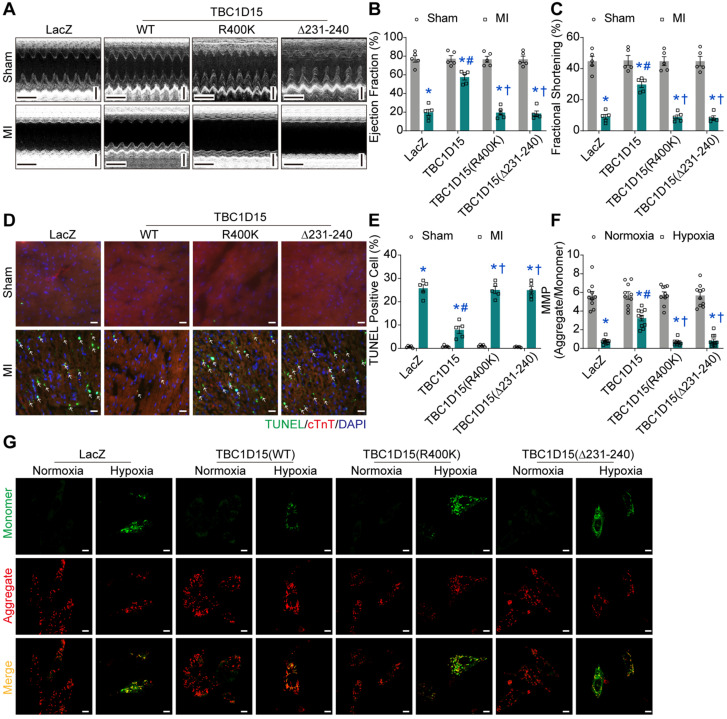
Figure 7.
Fis1 binding and RAB7-GAP domains are indispensable for TBC1D15-dependent cardioprotective effects. A-C. Decreases of ejection fraction and fractional shortening after 3-day MI were attenuated by TBC1D15 overexpression, but not by mutant TBC1D15 (R400K) or TBC1D15 (Δ231-240) (n = 5). Representative echocardiographic images (Scale bar = 200 ms-horizontal and 2 mm-vertical) are displayed; D-E. Increase of myocardial apoptosis after 3-day MI was alleviated by TBC1D15 overexpression, but not by mutant TBC1D15 (R400K) or TBC1D15 (Δ231-240) (n = 5). Representative TUNEL/cTnT/DAPI staining images (Scale bar = 25 µm) are shown. The white arrows indicate TUNEL positive nuclei. Mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05 vs. corresponding Sham group; # p < 0.05 vs. MI-LacZ group; † p < 0.05 vs. MI-TBC1D15 group; F-G. Cardiomyocytes mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) loss following 9-h hypoxia was ameliorated by TBC1D15 overexpression, but not by mutant TBC1D15 (R400K) or TBC1D15 (Δ231-240) (n = 10). Representative images of JC-1 staining (Scale bar = 10 µm) are exhibited. Mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05 vs. corresponding Normoxia group; # p < 0.05 vs. Hypoxia-LacZ group; † p < 0.05 vs. Hypoxia-TBC1D15 group.