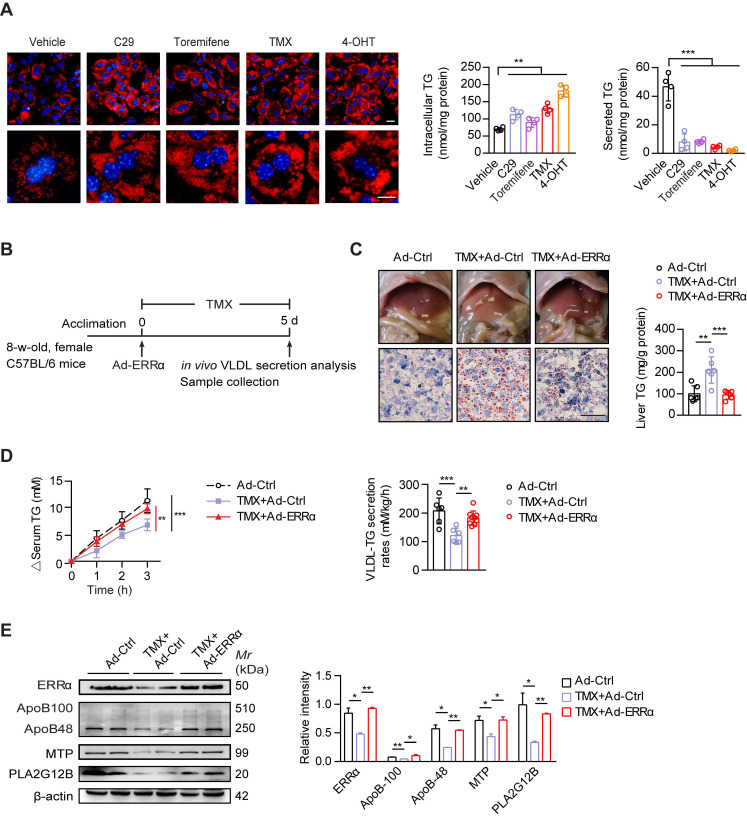
Figure 6.
ERRα overexpression protects against TMX-induced hepatic VLDL dysfunction and NAFLD in female mice. (A) Representative fields, intracellular TG contents and secreted TG of female C57BL/6 mice hepatocytes treated with C29, TMX, toremifene and 4-OHT (n = 4). LDs were labeled with Nile Red (red). Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Schematic of the experimental procedure of TMX-induced NAFLD in female mice. (C) Representative images of liver tissue (top), sections stained with Oil Red O (bottom) and liver TG levels from Ad-ERRα or Ad-Ctrl-injected female mice treated with TMX for 5 days (n = 6 mice). Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Analysis of VLDL-TG secretion (left panel) and rates (right panel) in treated female mice (n = 6 mice per group for Ad-Ctrl and Ad-Ctrl+TMX; n = 9 mice for Ad-ERRα+TMX group). (E) Western blots showing the indicated protein expression in liver tissues from Ad-ERRα or Ad-Ctrl-injected female mice treated with TMX (left panel). Densitometry analysis of the western blotting data normalized to the intensity of β-actin (right panel). Data presented as means ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t test for paired groups (A), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc (C and E) or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis (D). Abbreviations: C29, compound 29; TMX, tamoxifen; 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen; TG, triglyceride.