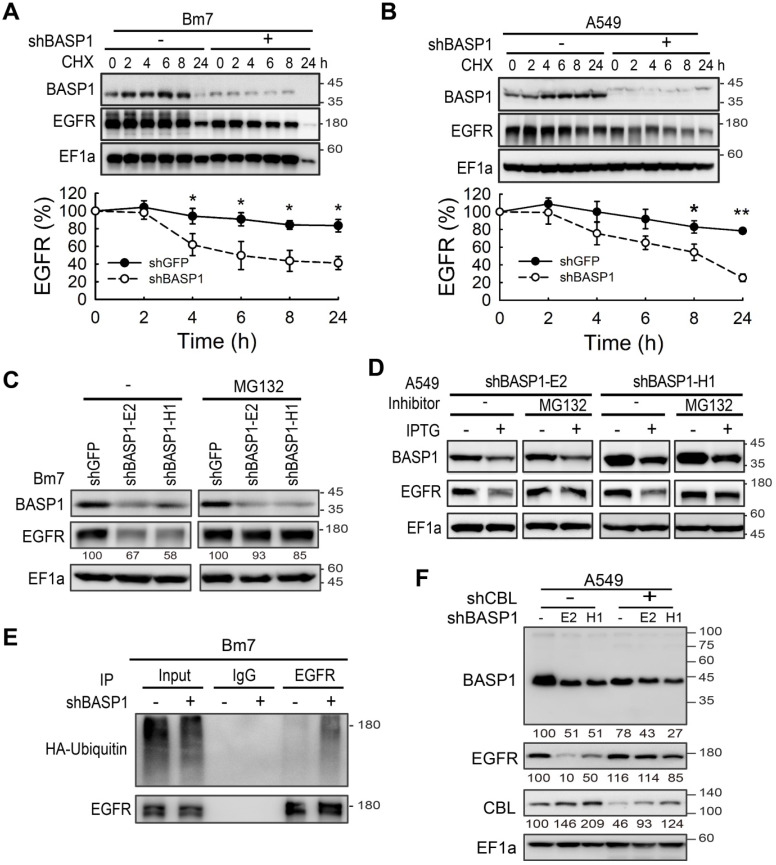
Figure 4.
BASP1 reduces ubiquitin-mediated EGFR degradation. (A and B) BASP1 knockdown enhanced EGFR protein degradation. Control and BASP1-knockdown Bm7 (A) and A549 lung cancer cells (B) were treated with 100 µM cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time periods. Western blot of BASP1 and EGFR. Relative EGFR expression was determined by measuring the EGFR band density from three independent experiments. Data represent the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, student's t-test. (C) Control and BASP1-knockdown Bm7 lung cancer cells were cultured under starvation for 16 hours and then treated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 2 hours before collecting cell lysates. Cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (5 µM) for 3 hours before EGF stimulation. (D) Control and IPTG-induced BASP1 knockdown A549 lung cancer cells were cultured under starvation for 16 hours and then treated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 2 hours before collecting cell lysates. Cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (5 µM) for 3 hours before EGF stimulation. (E) IPTG-induced shBASP1 of Bm7 cells with HA-ubiquitin overexpression followed by MG132 and EGF treatment for 2 hours. EGFR was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using an EGFR antibody. (F) Western blot of BASP1, EGFR, and CBL in control and BASP1-knockdown cells transiently transfected with shRNA against CBL.