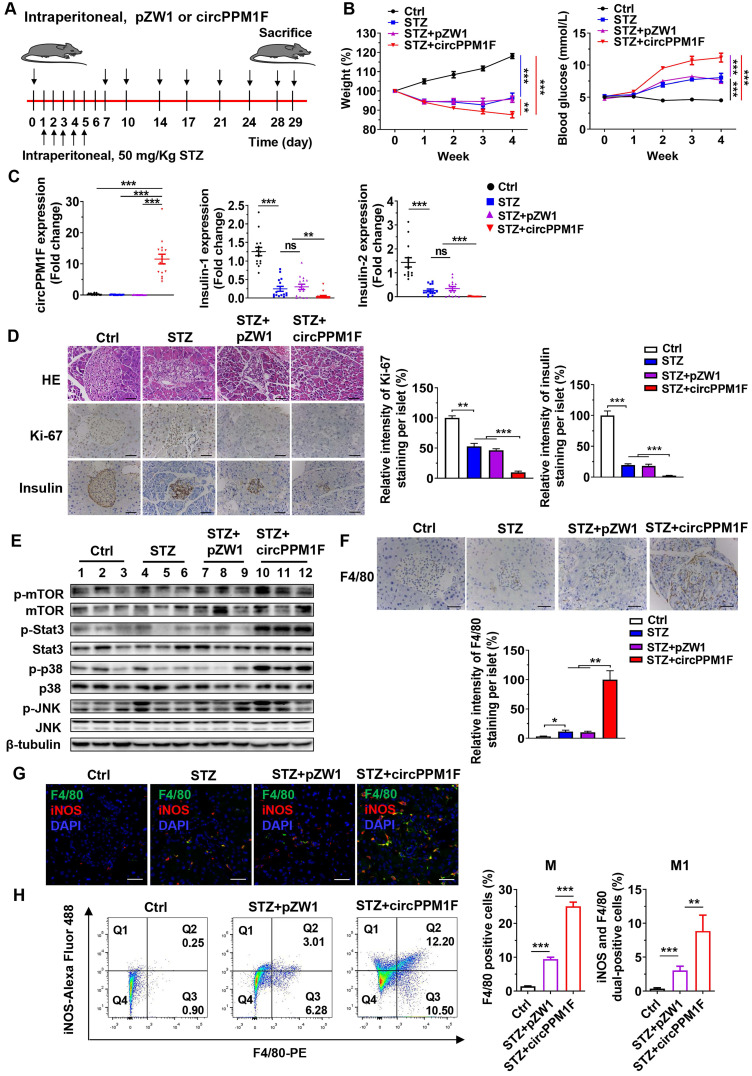
Figure 6.
circPPM1F facilitates pancreatic islet injury in diabetic mice through M1 macrophage activation. A. Treatment of circPPM1F in the STZ-induced diabetic mouse model (15 mice per group). B. Mean weekly body weight (left) and fasting blood glucose (right) change in four-group mice. C. Levels of circPPM1F and insulin in pancreas tissues were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). D. Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained pancreas tissues, immunohistochemistry (IHC) images of Ki-67 and insulin expression in pancreatic islets from experimental mice. Scale bar indicates 50 µm. Semi-quantification of Ki-67 and insulin staining of per islet were done by using Image J software. E. The levels of total p38, JNK, Stat3, mTOR, and their corresponding phosphorylated forms in pancreas tissues from experimental models were quantified by western blot. F. Representative IHC images of F4/80 expression in pancreatic islets from experimental mice. Scale bar indicates 50 µm. Semi-quantification of F4/80 staining of per islet were done by using Image J software. G. Immunofluorescence staining of infiltrated F4/80+/iNOS+ M1 macrophages in mice pancreatic islets. Green represents anti-F4/80 Ab; red represents anti-iNOS Ab; yellow represents F4/80 and iNOS merged; blue represents DAPI. Scale bar indicates 50 µm. H. The percentages of M1 macrophages in pancreas tissue cells from STZ-treated mice with or without circPPM1F overexpression and control mice were determined by flow cytometry (left). Quantification analyses of macrophages (F4/80+) and M1 macrophages (F4/80+/iNOS+) in pancreas tissue cells (right). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.