Figure 3. The E4872Q+/− Mutation Prevents Memory Loss and LTP Impairment of 5xFAD+/− Mice.
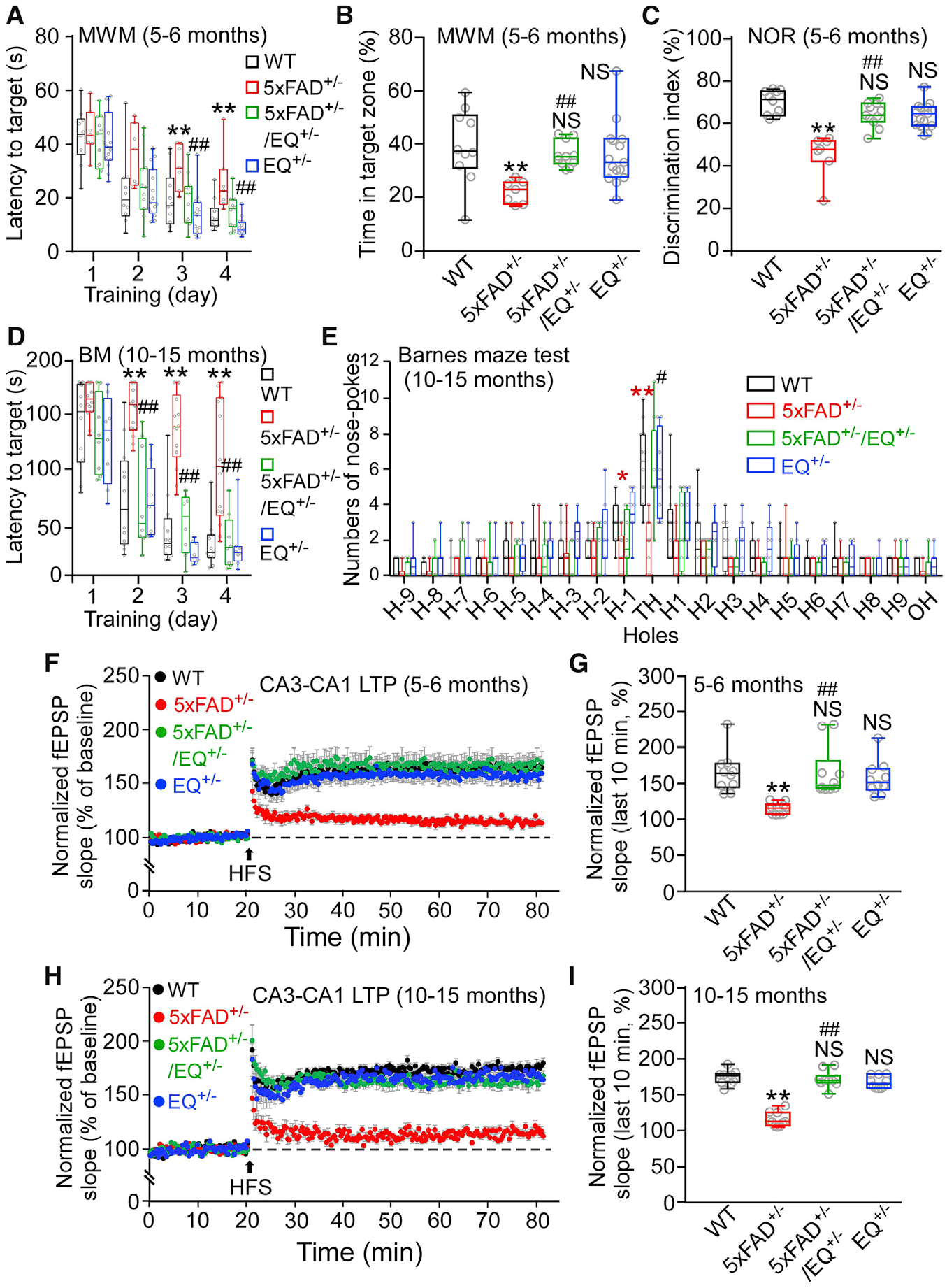
(A) The latency to reach the target platform of 5- to 6-month-old WT (n = 10), 5xFAD+/− (n = 7), 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− (n = 11), and EQ+/− (n = 15) mice in the Morris water maze (MWM) test.
(B) The time spent in the target quadrant.
(C) The percentage of time spent on the novel object in the novel object recognition (NOR) test in 5- to 6-month-old WT (n = 10), 5xFAD+/− (n = 7), 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− (n = 11), and EQ+/− (n = 15) mice.
(D) The latency to reach the target hole of 10- to 15-month-old WT (n = 12), 5xFAD+/− (n = 14), 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− (n = 8), and EQ+/− (n = 8) mice in the Barnes maze (BM) test.
(E) The number of nose pokes to each hole on the BM test platform (**5xFAD versus WT).
(F) Effect of 100-Hz high-frequency stimulation (HFS) on the mean Schaffer collateral-evoked fEPSP slope in hippocampal slices from 5- to 6-month-old WT (10 mice, 20 slices), 5xFAD+/− (10 mice, 20 slices), 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− (10 mice, 20 slices), and EQ+/− (10 mice, 20 slices) mice.
(G) The averaged normalized fEPSP slope.
(H) Effect of HFS on the fEPSP slope of 10- to 15-month-old WT (10 mice, 20 slices), 5xFAD+/− (10 mice, 20 slices), 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− (10 mice, 20 slices), and EQ+/− (10 mice, 20 slices) mice.
(I) The averaged normalized fEPSP slope.
Data shown are the median and range (Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn-Bonferroni post hoc test; *p < 0.5, **p < 0.01 versus WT, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01; 5xFAD+/−/EQ+/− versus 5xFAD+/−). See also Figures S4 and S5.
