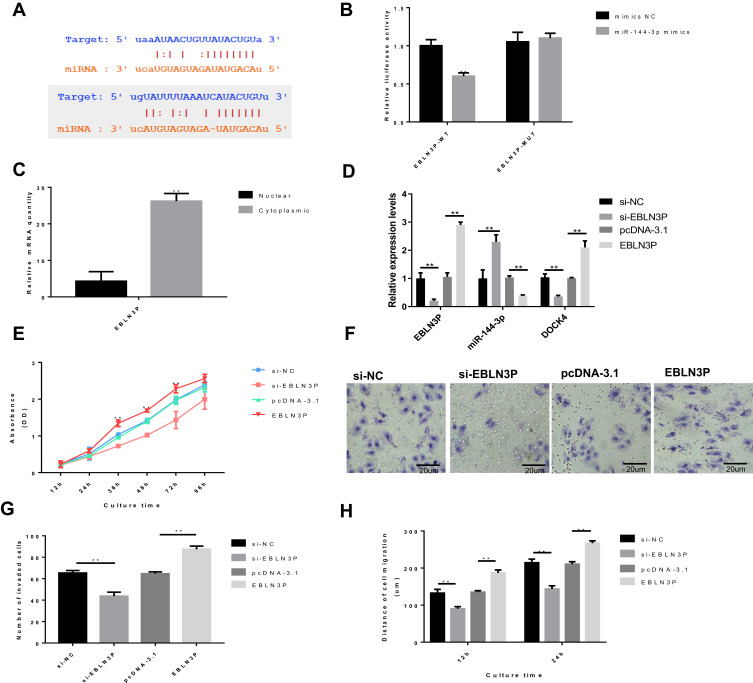
Figure 1.
EBLN3P knockdown inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of liver cancer cells in vitro. HepG2 cells were transfected with EBLN3P-targeted siRNA (si-EBLN3P), negative control siRNA (si-NC), pcDNA3.1-EBLN3P overexpression vector (pcDNA-EBLN3P) or blank vector plasmid (pcDNA-3.1). (A) Bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that EBLN3P can directly interact with miR-144-3p (up) and that miR-144-3p can directly bind to the 3ʹ-UTR regions of DOCK4 (down). (B) Dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed to verify the impact of miR-144-3p on the luciferase signal of reporter plasmids containing EBLN3P. (C) The nuclear and cytoplasmic expression levels of EBLN3P in HepG2 cells. (D) The expression levels of EBLN3P and miR-144-3p were explored via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (E) Cell proliferation was tested by the Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. (F) The number of invaded cells. (G) Cell invasion was detected by the Transwell assay. (H) Cell migration was detected by the wound healing assay. That data is shown as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01.
Abbreviations: siRNA, small interfering RNA; miR, microRNA