FIGURE 1.
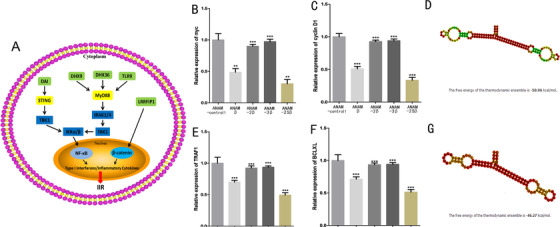
Innate immune response to cytosolic DNA and the inhibitory effects of ANAMs on targeted molecules in 5637 cells. A, DNA sensors (green) activate the downstream kinases (yellow) once they bind to cytosolic DNA. The transcription factors (β‐catenin, NF‐κB) are activated by a series of phosphorylation events, translocate to the nucleus, and induce the expression of type 1 interferon and inflammatory cytokines, which are then secreted and transmit innate immune responses to other cells. B, qPCR was used to evaluate the inhibitory effects of ANAMs on β‐catenin and NF‐κB. Inhibitory effects of ANAM‐β, ANAM‐2β, ANAM‐3β, and ANAM‐2Sβ on the expression of myc in 5637 cells. C, Inhibitory effects of ANAM‐β, ANAM‐2β, ANAM‐3β, and ANAM‐2Sβ on the expression of cyclin D1 in 5637 cells. D, Secondary structure and nucleic acid sequence of ANAM‐2Sβ. The structure was colored by base‐pairing probabilities. Pale colors indicate that a base‐pair cannot be formed in some sequences of the alignment. E, Inhibitory effects of ANAM‐κB, ANAM‐2κB, ANAM‐3κB, and ANAM‐2SκB on the expression of TRAF1 in 5637 cells. F, Inhibitory effects of ANAM‐κB, ANAM‐2κB, ANAM‐3κB, and ANAM‐2SκB on the expression of Bcl2X in 5637 cells. G, Secondary structure and nucleic acid sequence of ANAM‐2SκB. All experiments were repeated three times. ** P < .05, *** P < .001 compared to the ANAM control group
