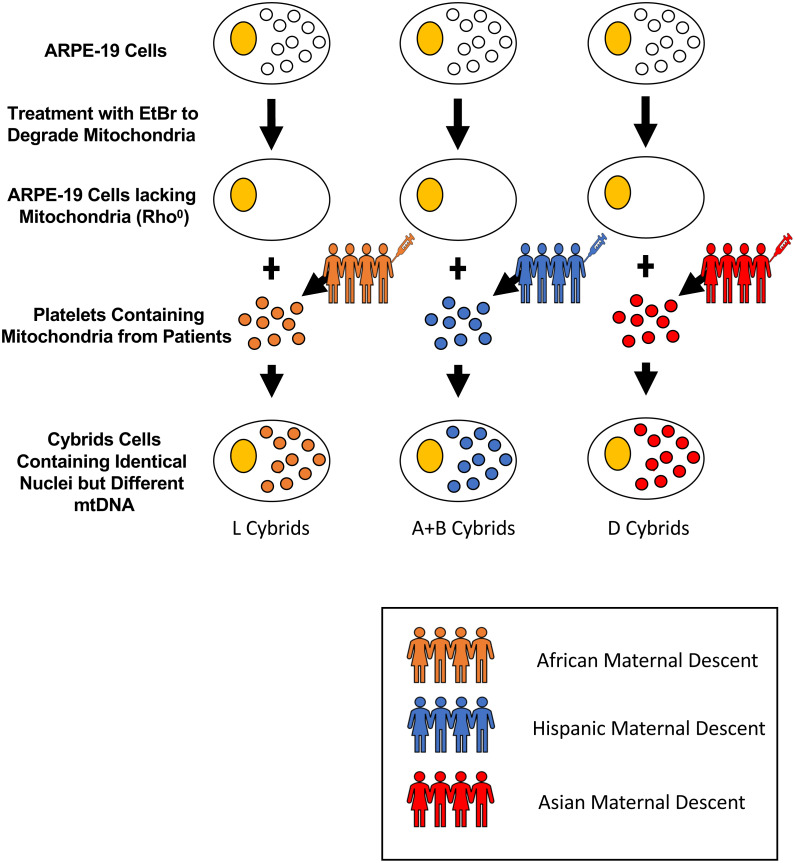
Figure 1. Creation of cybrid cells with identical nuclei but varying mtDNA.
Cytoplasmic hybrids (cybrids) were created by fusing ARPE-19 Rho0 (mtDNA free) cells with platelets isolated from peripheral blood from individuals of either L (African), [A+B] (Hispanic), or D (Asian) maternal descent. Rho0cells were initially obtained by treating ARPE-19 cells with small doses of Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) over many passages until they lacked mitochondria. Once the cells were depleted of their mitochondria, they were fused with the obtained platelets using polyethylene glycol fusion. These platelets lacked nuclear (n) DNA, and only contained mitochondrial (mt) DNA. Once fused, the created cybrids contained identical nDNA and the particular mtDNA obtained from the specified patient’s platelets. The mtDNA haplogroups for each subject and cybrid cell line were identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) along with restriction enzyme digestion and mtDNA sequencing.