Fig. 3.
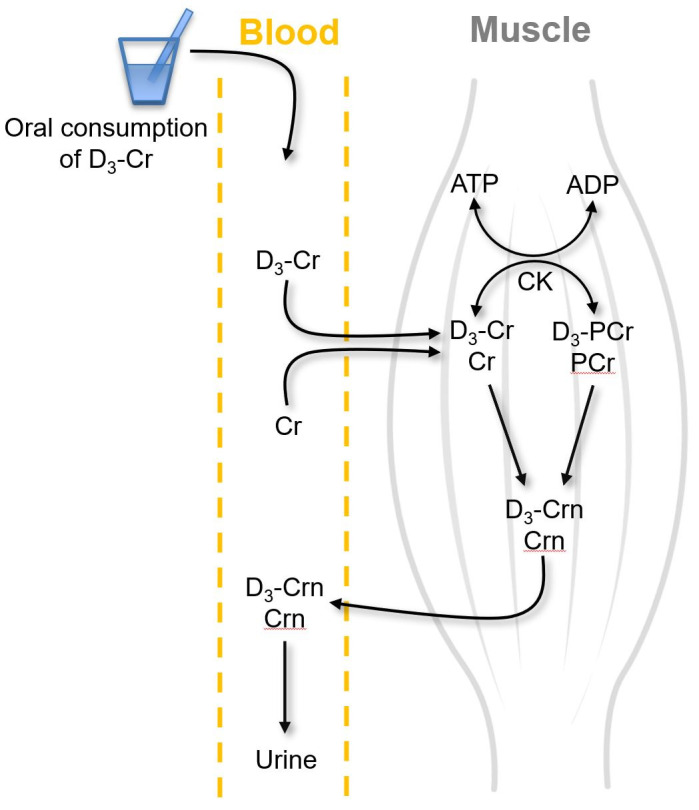
D3-creatine dilution method. Orally consumed D3-creatine (D3-Cr) is absorbed into the circulation and transported into muscles, where it equilibrates with existing unlabeled Cr (i.e., dilution of D3-Cr in unlabeled Cr). Both labeled and unlabeled Cr are phosphorylated to form phosphocreatine (PCr) via the enzymatic action of creatine kinase (CK). Both Cr and PCr are spontaneously converted to creatinine (both labeled and unlabeled Crn) at a constant rate. Crn (both labeled and unlabeled) is then released to the blood and ultimately excreted in the urine. The urine Crn enrichment (ratio of labeled to unlabeled Crn) is equal to the D3-Cr enrichment in muscle. Information on the doses of orally consumed D3-creatine, urine Crn enrichment, and Cr mass per kg muscle mass is used to calculate the muscle mass.
