Fig. 3.
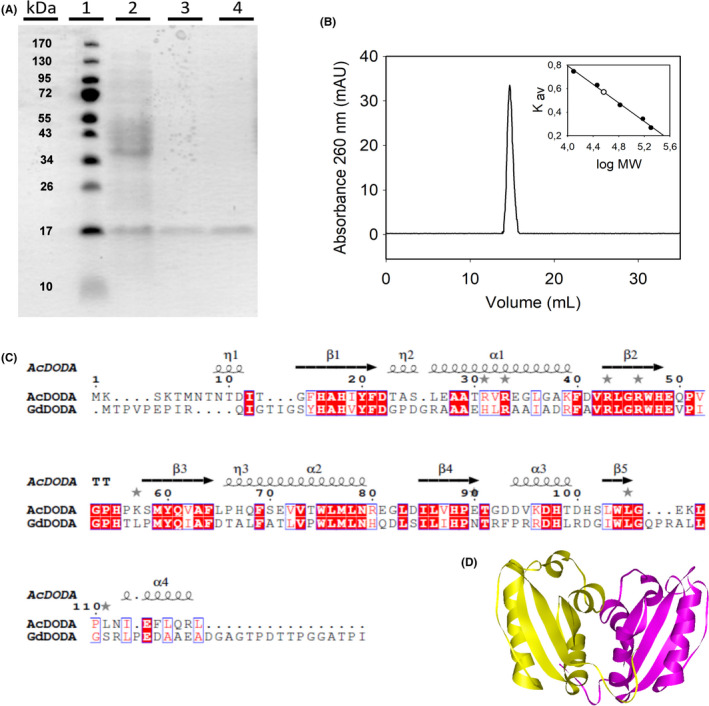
Characterization of DODA enzyme from Anabaena cylindrica.
A. SDS‐PAGE electrophoretic analysis of the expression and purification of AcDODA from E. coli BL21 cells. Lane 1, molecular weight markers; lane 2, soluble protein content of cells harvested 20 h after IPTG induction (0.1 mM); lane 3, eluted protein after affinity chromatography purification; and lane 4, final purified protein obtained after desalting on PD‐10 columns.
B. Analysis of the AcDODA enzyme by gel filtration chromatography. Elution was followed at a wavelength of λ = 260 nm. Inset: Calibration curve and molecular mass determination of the detected dimer.
C. Comparison of DODA sequences from A. cylindrica and G. diazotrophicus. Sequence alignment with structural considerations was performed with Expresso (Armougom et al., 2006). Conserved blocks of amino acids are squared. Strictly conserved residues are shown in red.
D. Structural model for the dimer of DODA enzyme from A. cylindrica by using the template PDB‐ID 2PEB from Nostoc punctiforme. The two monomeric units are shown in yellow and purple.
