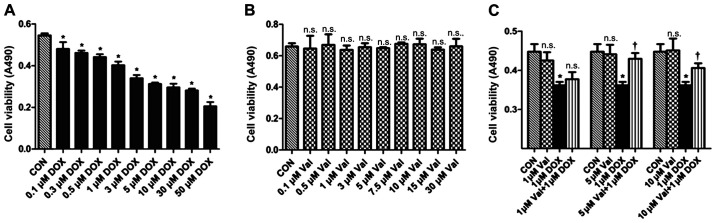
Figure 5.
Cell viability measured by MTT assay. (A) H9C2 cells were treated with various concentrations of DOX for 24 h, DOX resulted in cell death in a dose-dependent manner. Cell viability significantly decreased with 1 µM DOX, so this concentration was chosen as the target dose. (B) H9C2 cells were treated with numerous concentrations of Val, the results revealed that the nine different concentrations of Val did not affect the survival of H9C2 cells within 24 h. (C) Val concentration required to protect against DOX-induced cytotoxicity was calculated by performing a dose-response study in the presence of 1, 5 and 10 µM Val. The cytotoxic effects of DOX were significantly attenuated by pre-treatment with 5 and 10 µM Val. Based on these results, 5 µM Val was selected as the target dose for further study. *P<0.05 vs. CON; †P<0.05 vs. DOX; n.s., not significant. CON, control; DOX, doxorubicin; Val, valsartan; NOX, NAD(P)H oxidase.