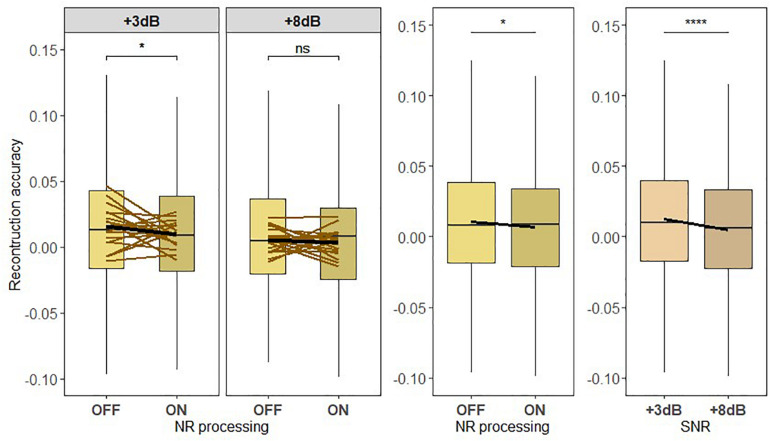
FIGURE 8.
(H3) The active NR processing reduces the neural representation of the background noise across low and high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) level. Boxplot showing the reconstruction accuracy values of the ignored background noise envelope reconstructed from the ignored noise decoder for two SNR levels tested with noise reduction (NR) scheme inactive (OFF) or active (ON; left column) for global averages across NR schemes (middle column) and for global averages across SNR levels (right column). A significant main effect of NR, indicating the reduced neural representation of the ignored background noise when NR scheme was turned on, and a significant main effect of SNR were observed. A significant difference in reconstruction performances between inactive and active NR in the pairwise comparison at lower SNR (+3 dB) was observed. The horizontal lines in yellow denote single participants and the horizontal lines in black depict predictions of linear mixed models. The black horizontal line in the boxplot denotes the mean reconstruction accuracy of the ignored background noise envelope and the box indicates the upper and the lower quartiles, with the vertical lines representing the minimum and the maximum reconstruction accuracy values. The asterisk indicates significant differences (*p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0005); ns, not significant.