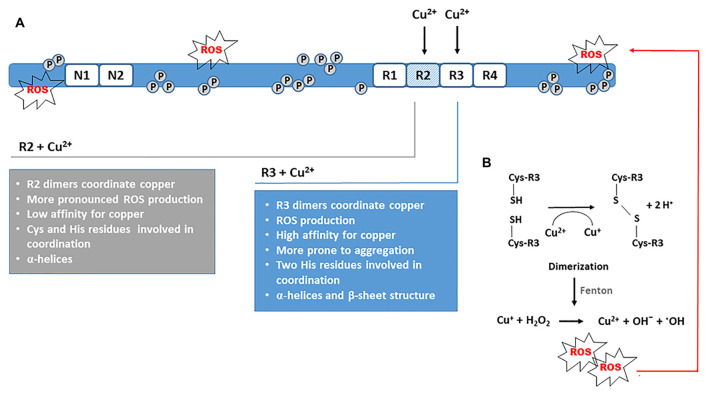
Figure 3.
Catalytic role of Cu2+ in disulfide bond formation and dimerization. (A) In vitro aggregation of tau fragments derived from the R2 and R3 repeat units demonstrates the ability of copper to stimulate the formation of PHF-like fibrils. Aggregation is promoted in OS conditions. (B) Dimerization via disulfide bond formation between Cys residues is the critical initiating step that triggers tau oligomerization and further formation of fibrillar forms. Concomitantly, Cu2+ is reduced to Cu+, which catalyzes Fenton reaction and production of hydroxyl radicals. The ROS generated induces additional oxidative damage of tau protein promoting its polymerization.