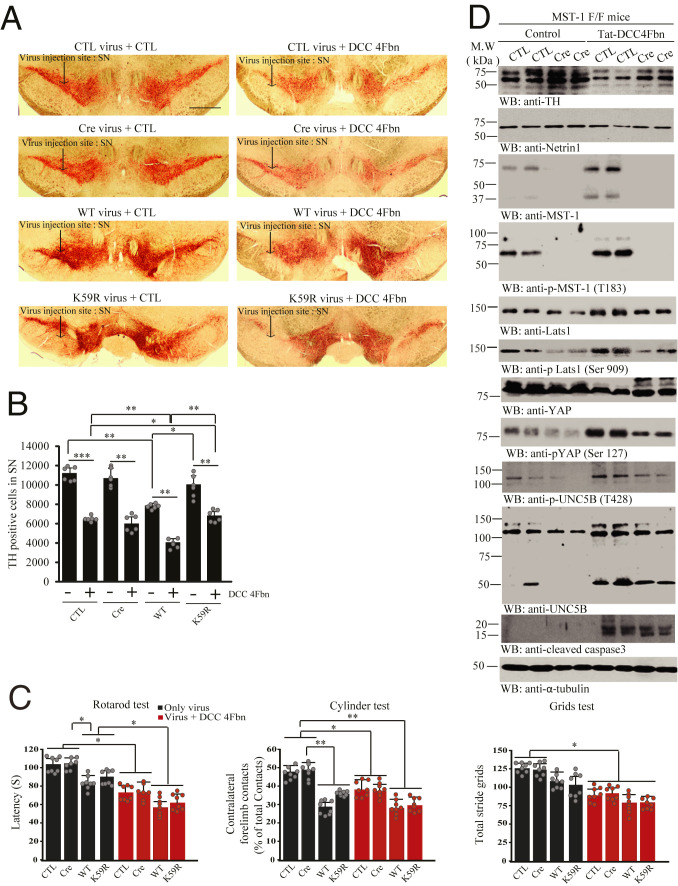
Fig. 6.
MST1 kinase activity is required for DCC-4Fbn-induced dopaminergic neuronal loss and motor dysfunctions in MST1 f/f mice. (A) IHC staining of TH in the SN of MST1 f/f mice. Control, Cre, MST1 WT, or MST1 K59R virus was injected into the SN regions of MST1 f/f mice, followed by treatment with Tat-DCC-4Fbn (i.p.). Dopaminergic neuronal loss in the brain (SN) was analyzed by TH IHC analysis. (Scale bar: 2,000 μm.) (B) Quantification of TH-positive neurons. The bar graph is stereological counted TH-positive cells quantified result; n = 6 independent experiments. (C) Motor behavioral assays; n = 8 each group. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni test for multiple group comparison. *P < 0.05; **< 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (D) Deletion of MST1 decreases DCC-4Fbn−stimulated TH loss. Immunoblot analysis of TH, NTN1, MST1, p-MST1(T183), LATS1, p-LATS1(Ser909), YAP, p-YAP(Ser127), UNC5B, p-UNC5B(T428), and cleaved caspase-3 levels in control (CTL) or Cre virus-injected MST1 f/f brain (SN) lysate samples. Three independent experiments were conducted.