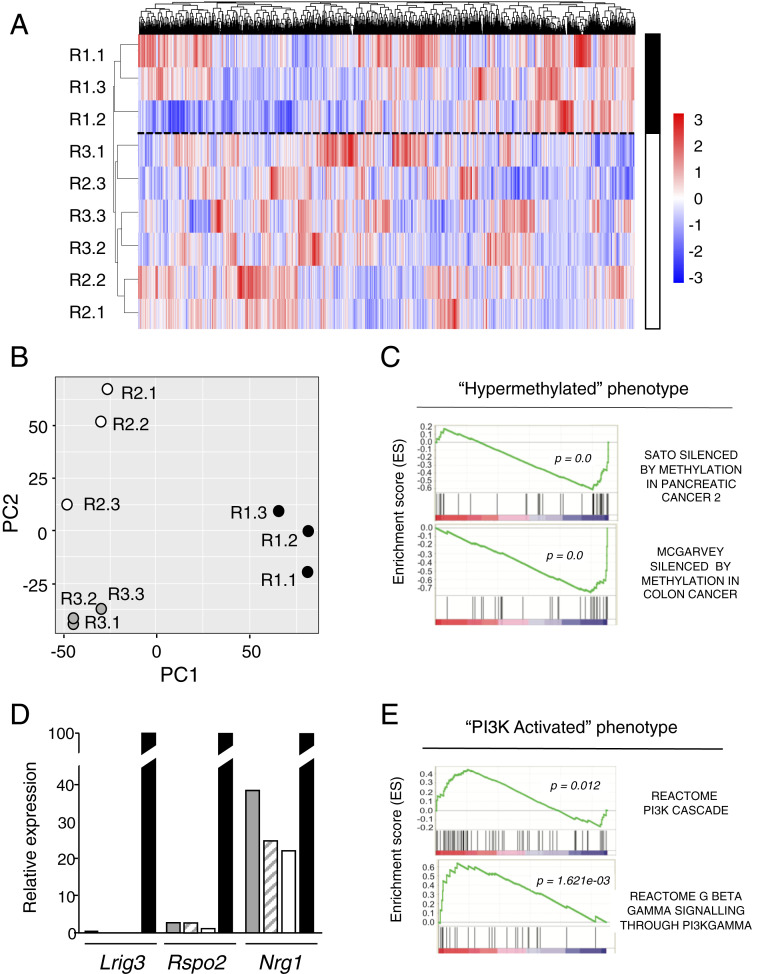
Fig. 6.
Resistance to CDK4/RAF1 inactivation is mediated by independent mechanisms. (A) Heatmap representing color-coded expression levels of differentially expressed genes among the indicated CDK4/RAF1 resistant tumor cell clones. The solid and open bars separated by a discontinuous line indicate the two main hierarchical clusters found among these resistant clones. (B) Distribution of the 9 CDK4/RAF1-resistant tumor cell clones in a 2D space determined by the first and second principal components generated by PCA. (C) GSEA for the "hypermethylated" phenotype comparing resistant clones R1.1, R1.2, and R1.3 with their parental T1 cell lines before CDK4/RAF1 inactivation. Adjusted P < 0.05. (D) Validation of the three main down-regulated genes Lrig3, Rspo2, and Nrg1, in CDK4/RAF1-resistant tumor cell clones exhibiting a "hypermethylated" phenotype. Expression levels were determined by RT-PCR in CDK4/RAF1 resistant tumor cell clones R1.1 (gray bars), R1.2 (striped bars), R1.3 (open bars) relative to those present in the parental T1 cells (solid bars). (E) GSEA for the "PI3K-activated" phenotype comparing resistant clones R2.1, R2.2, and R2.3 as well as R3.1, R3.2, and R3.3 with their parental cell lines T2 and T3, respectively, before CDK4/RAF1 inactivation. Adjusted P < 0.05.