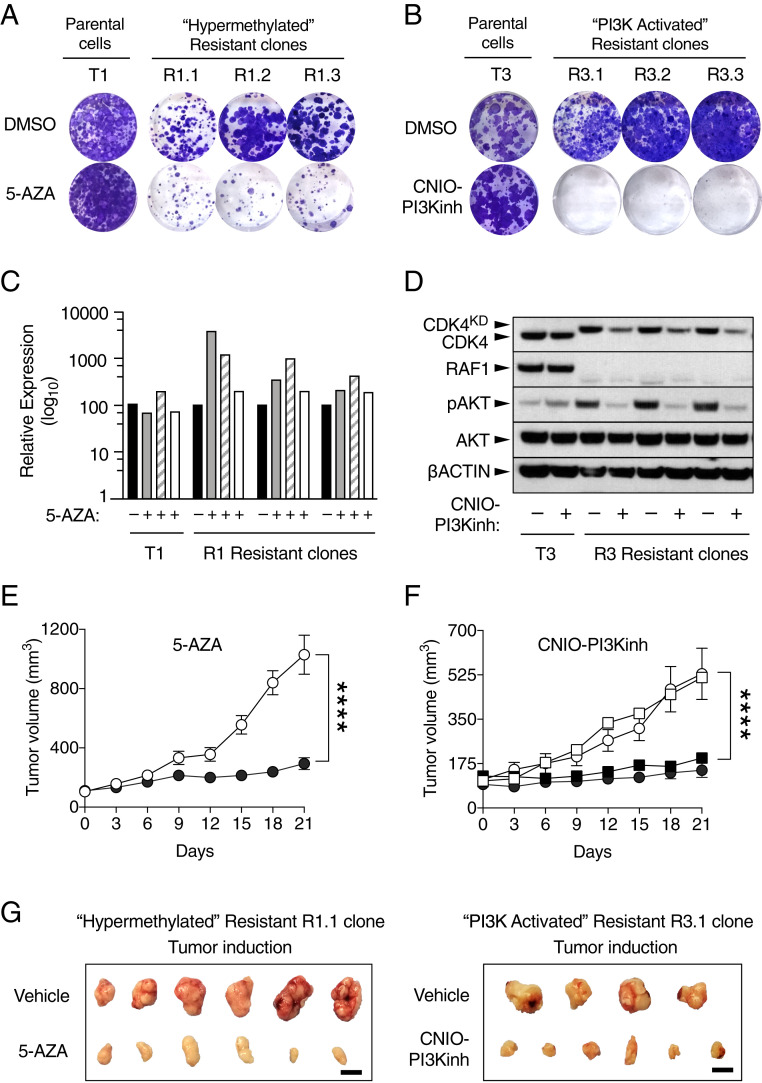
Fig. 7.
Pharmacological validation of the hypermethylated and PI3K-activated resistance mechanisms. (A) Colony formation assay of the parental T1 cell line and the CDK4/RAF1 hypermethylated resistant clones R1.1, R1.2, and R1.3 treated with DMSO or with 2 µM 5-AZA for 9 d. (B) Colony formation assay of the parental T3 cell line and CDK4/RAF1 PI3K-activated resistant clones R3.1, R3.2, and R3.3 treated with DMSO or with 1 µM PI3K inhibitor (CNIO-PI3Kinh) for 9 d. (C) RT-PCR validation of the levels of expression of Lrig3 (gray bars), Rspo2 (striped bars), and Nrg1 (open bars) after 72 h in the absence or presence of 5-AZA relative to those in the DMSO treated cells (solid bars) in T1 parental cells and R1 resistant clones. (D) Western blot analysis of CDK4, CDK4KD, RAF1, phospho-AKT (pAKT), and AKT expression after 24 h in the absence or presence of the PI3K inhibitor (CNIO-PI3Kinh) in T3 parental cells and R3 resistant clones. β-Actin was used as loading control. Migration of the above proteins is indicated by arrowheads. (E) Tumor growth of CDK4/RAF1 resistant clones R1.1 and R1.2 treated with vehicle (empty circles; n = 15 tumors) or with 6 mg/kg of 5-AZA (solid circles; n = 15 tumors) for 21 d. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using the unpaired Student’s t test. ****P < 0.0001. (F) Tumor growth of CDK4/RAF1-resistant clones R2.1 (circles) and R3.1 (squares) treated with vehicle (open symbols) (R2.1, n = 8 tumors and R3.1, n = 9 tumors) or with 15 mg/kg of PI3K inhibitor (CNIO-PI3Kinh) (solid symbols) (R2.1, n = 9 tumors and R3.1, n = 8 tumors) for 21 d. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM P values were calculated using the unpaired Student’s t test. ****P < 0.0001. (G) Representative pictures of tumors derived from CDK4/RAF1-resistant clone R1.1 treated with vehicle or with 5-AZA and of tumors derived from CDK4/RAF1-resistant clone R3.1 treated with vehicle or with the PI3K inhibitor (CNIO-PI3Kinh). (Scale bar, 1 cm.)