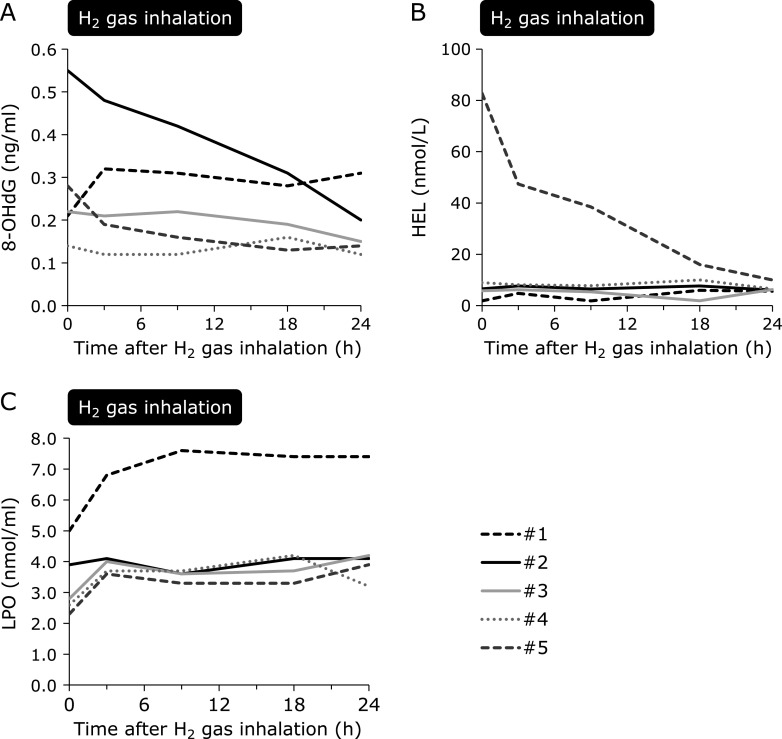
Fig. 3.
Temporal changes in plasma oxidative stress markers in patients with post-cardiac arrest syndrome treated with H2 gas inhalation. Each line indicates an individual patient. (A) 8-OHdG, a marker of DNA damage, was decreased, except for in one patient with sepsis, from 0.30 ± 0.18 ng/ml to 0.15 ± 0.03 ng/ml before H2 gas inhalation and at 24 h, respectively (p = 0.31). (B) HEL, an early marker of lipid peroxidation, decreased dramatically in one patient, but remained the same in other patients (p = 0.39). (C) LPO, a marker of lipid peroxidation, slightly increased within 3 h after the initiation of H2 gas inhalation (p = 0.05, 0 h vs 3 h), but was then maintained for 24 h (p = 0.96, 3 h vs 24 h). LPO was markedly high in the patient with sepsis. 8-OHdG, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine; H2, molecular hydrogen; HEL, Nɛ-hexanoyl-lysine; LPO, lipid hydroperoxide.