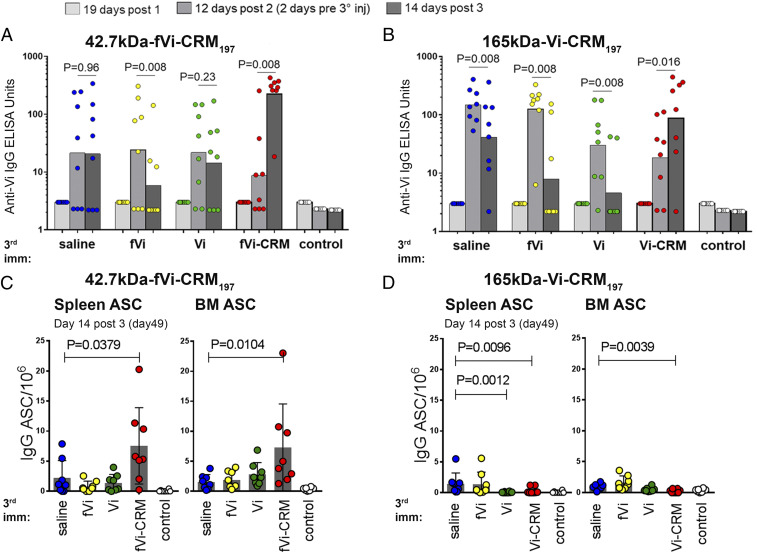
Fig. 2.
The effects of Vi size in a Vi-CRM197 conjugate vaccine on the induction of Vi-specific IgG antibodies and ASCs in spleen and their homing to the BM. Neonatal mice were immunized with two doses of 42.7-kDa fVi-CRM197+alum (Left) or 165-kDa Vi-CRM197+alum (Right) at 3-wk intervals and then boosted 2 wk after the second dose with saline (blue circles), unconjugated 42.7-kDa fVi (yellow circles), unconjugated 165-kDa Vi (green circles), or comparable conjugates as in the first immunizations (red circles), all boosters without alum. (A and B) Vi-specific IgG response expressed in ELISA units in sera from mice primed with 42.7-kDa fVi-CRM197 (A) or 165-kDa Vi-CRM197 (B). Individual mice are represented by the dots; column heights represent geometric mean units. (C and D) Vi-specific IgG+ ASCs measured at 49 d after the first immunization with 42.7-kDa fVi-CRM197 (C) or 165-kDa Vi-CRM197 (D) in spleen (Left) and BM (Right). Results are expressed as number of spots/106 cells (mean ± SD) in spleen or BM; individual mice are represented by the dots. Statistical difference was calculated using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, where antibody levels were compared 2 d before and 14 d after booster (A and B), and the Mann–Whitney U test, where 42.7-kDa fVi, 165-kDa Vi, and 42.7-kDa fVi-CRM197/165-kDa Vi-CRM197 boosters were compared with saline booster (C and D).