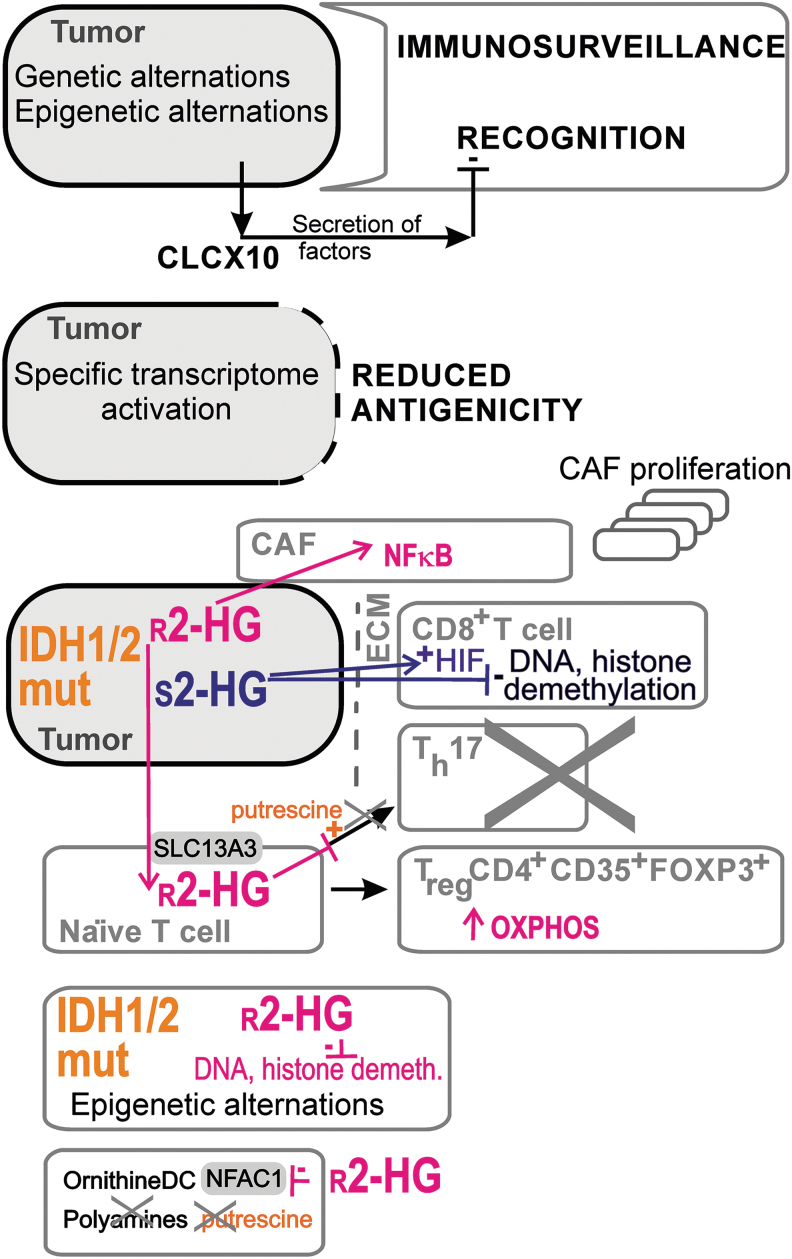
FIG. 6.
2HG effects related to immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. The scheme summarizes the major effects of 2HG within the tumor microenvironment: prevention of tumor recognition (top): r-2HG inhibits the secretion of certain factors such as CXCL10. In this way, r-2HG prevents the recruitment of T cells and hence tumor recognition (84, 101). Reduction of antigenicity (second from the top): can reset epigenetic and gene expression changes promoted by 2HG. Promoting proliferation of CAF (third from the top). Impairment of immune cells and their differentiation (remaining schemes): such as the promotion of Treg cells and the simultaneous blockage of differentiation into the helper Th17 cells from the naive T cells; plus effects on HIF transcriptome reprogramming and epigenetics alternations, as was described for tumor cells. Bottom: an example of the blockage of polyamine expression due to r-2HG inhibition of the NFATC1 (18). CAF, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; NFATC1, nuclear factor of activated T cells 1; Th, T helper.