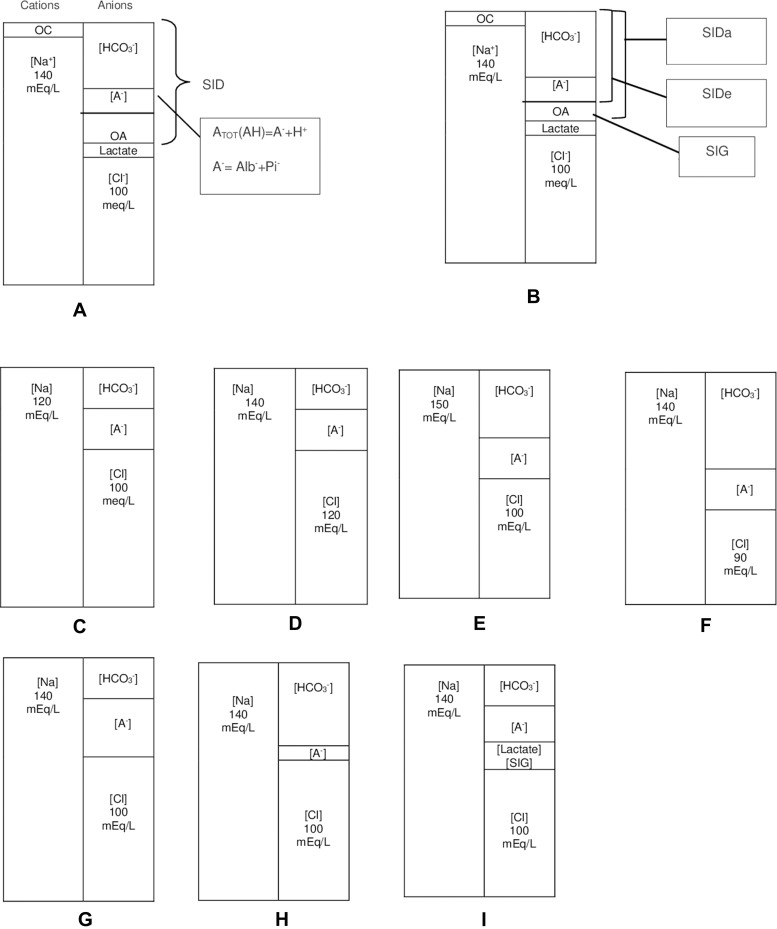
Figure 1.
Simplified illustration of normal acid-base status and metabolic acid-base disturbances with gamblegrams based on the Stewart approach. (A–B) Normal states: As a result of the electroneutrality law, the concentration of total cations is equal to that of total anions. While strong ions dissolve in water completely, weak ions only dissolve partially. There are two major strong ions in the ECF—[Na] as the cation and [Cl] as the anion. Strong cations besides [Na], such as [K], [Ca], [Mg], [Li], [Al], and others, are represented as OC. Moreover, OA represents other strong anions besides Cl and lactate. OA contains strong anions, including ketone, sulfate, acetate, and others. The difference between all strong cations and all strong anions is known as [SID]. Since Na and Cl are the principal ions of the ECF,[SID] can be simplified as the difference between Na and Cl. In order to preserve electroneutrality, [A TOT] and [HCO3] fill the space formed by the SID. SIDa is simply calculated as Na–(Cl+Lactate), and SIDe is the sum of A− + HCO3. A− is the dissociated part of ATOT that indicates [Alb−]+ [Pi−]. Additionally, SIG is the difference between SIDa and SIDe. Notably, while SIDa is a calculated parameter, SIDe is a measured one. OA also represents SIG. (C) The reduced SID due to water surplus or sodium loss. (D) Hyperchloremic acidosis: SID is narrowed due to the presence of excess chloride. (E) Hypernatremic alkalosis: SID is widened due to sodium surplus or water loss. (F) Hypochloremic alkalosis: SID is increased due to chloride loss. (G) Increased [ATOT] due to hyperphosphatemia or hyperalbuminemia squeezes [HCO3] and, subsequently, acidosis. (H) Hypoalbuminemia or hypophosphatemia widened [HCO3] with a decrease in [A TOT], resulting in alkalosis. (I) Lactic acidosis: Lactate is considered a strong anion that decreases SID upon accumulation; SIG acidosis; eg, ketoacidosis.
Abbreviations: mEq/L, milli equivalent per liter; OC, other cations; OA, other anions; ECF, extracellular fluid; [SID], strong ion difference; [SIDa], apparent SID; [SIDe], effective SID; [SIG], strong ion gap; AG, anion gap; [ATOT], total weak acid concentration; [Na], sodium; [K], potassium; [Li], lithium; [Ca], calcium; [Al], aluminium; [HCO3], bicarbonate; [Cl], chloride; [Alb], albumin; [Pi], inorganic phosphate.