Figure 28b.
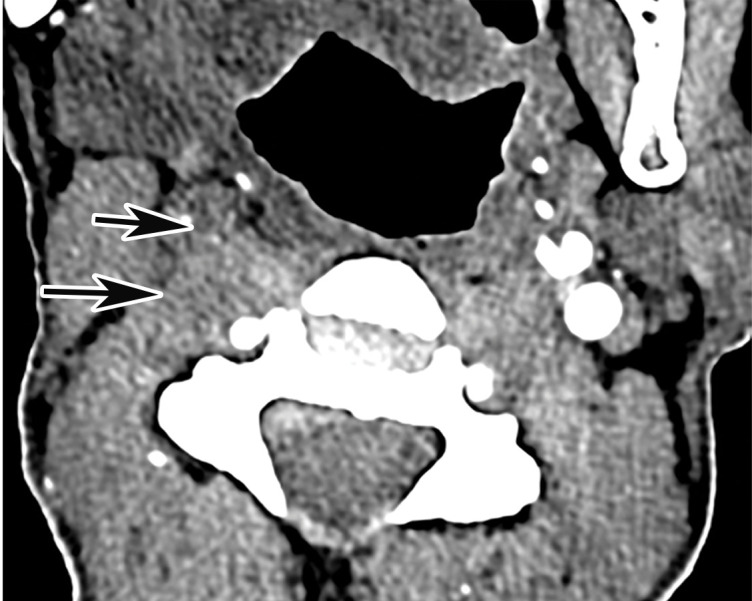
Common carotid artery (CCA) occlusion in a 56-year-old woman with neurologic deficits who had been hospitalized with COVID-19. (a, b) Coronal three-dimensional maximum intensity projection reformatted image (a) and axial CT angiographic image (b) of the head and neck show an abrupt cutoff at the origin of the CCA (black arrow in a). Note the absence of opacification of the right CCA, as well as internal and external carotid arteries (arrows in b). The left carotid vasculature is well opacified with intravenous contrast material (white arrow in a). (c) Axial nonenhanced head CT image shows wedge-shaped areas of hypoattenuation (arrows) in a watershed distribution, consistent with acute infarcts related to carotid occlusion.
