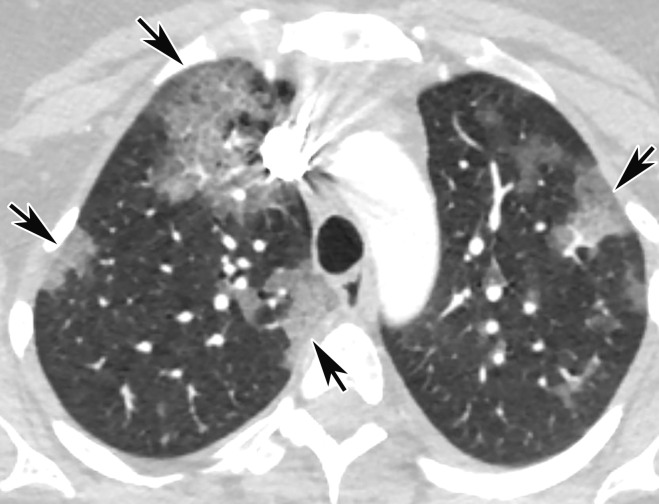
Figure 5a.
Temporal pulmonary changes of COVID-19 pneumonia at CT in a 36-year-old woman. (a–c) Axial contrast-enhanced CT images obtained at hospital admission show patchy bilateral GGOs and interlobular septal thickening (black arrows), with lower lobe predominance and subpleural involvement. Note also some immediate subpleural sparing of the GGOs (white arrows in b and c). (d–f) Follow-up corresponding axial contrast-enhanced CT images show evolving consolidative changes with volume loss, architectural distortion (ovals), and bronchiectasis (arrows in e and f).