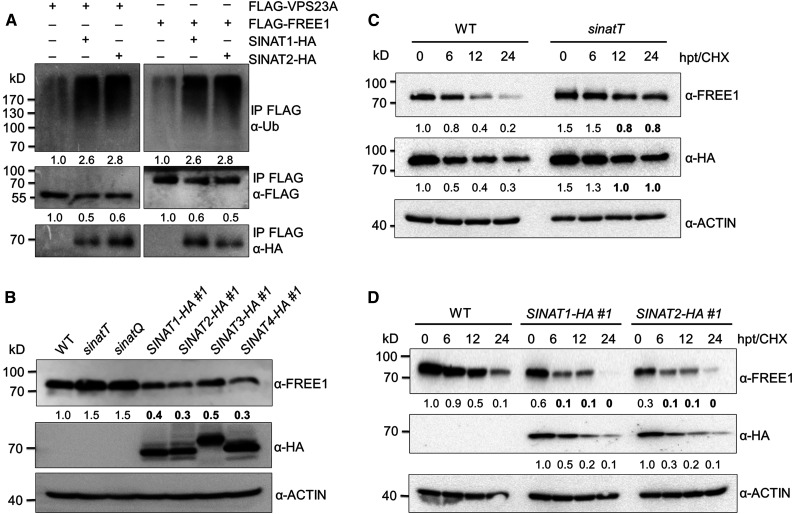
Figure 3.
SINATs Mediate Ubiquitination and Degradation of FREE1 and VPS23A.
(A) In vivo ubiquitination assays for VPS23A and FREE1. FLAG-tagged VPS23A and FREE1 were coexpressed with GFP-SINAT1-HA or GFP-SINAT2-HA, respectively, in the wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis protoplasts. Total protein from each sample was extracted in IP buffer and incubated with anti-FLAG magnetic beads. Proteins in the eluate were detected by anti-ubiquitin (Ub), anti-FLAG, and anti-HA antibodies. The relative intensities of Ub-FLAG-VPS23A, Ub-FLAG-FREE1, FLAG-VPS23A, and FLAG-FREE1 are shown below.
(B) FREE1 protein level in the wild-type (WT), sinat mutants, and SINAT overexpression lines. Total proteins were extracted from 7-d-old seedlings of WT, sinatT (sinat1 sinat2 sinat4), sinatQ (sinat1 sinat2 sinat3 sinat4), and SINAT-overexpression lines (SINAT1-HA #1, SINAT2-HA #1, SINAT3-HA #1, and SINAT4-HA #1). The anti-FREE1 and anti-HA antibodies were used in immunoblots to detect FREE1 and SINAT proteins.
(C) Protein stabilities of FREE1 and VPS23A in the sinatT mutant. Transgenic seedlings (7 d old) expressing HA-GFP-VPS23A in the wild-type (WT) or sinatT mutant backgrounds were treated with 500 μM CHX for the indicated times (0, 6, 12, and 24 h). Total proteins were extracted with IP buffer, and anti-FREE1 and anti-HA antibodies were used to detect FREE1 and HA-GFP-VPS23A, respectively.
(D) Degradation of FREE1 in SINAT-overexpression plants. The wild-type (WT), SINAT1-HA #1, and SINAT2-HA #1 seedlings (7 d old) were treated with 500 μM CHX for the indicated times (0, 6, 12, and 24 h).
Total proteins were extracted with IP buffer, and anti-FREE1 and anti-HA antibodies were used to detect FREE1 and GFP-SINATs-HA proteins, respectively. The level of ACTIN was used as a control. The relative intensities of FREE1, HA-GFP-VPS23A, and GFP-SINATs-HA proteins are shown below. The bold numbers show remarkably decreased protein levels compared with that of controls. Numbers on the left indicate the molecular weight (kD) of each band. hpt, hours post treatment.