Figure 1.
Peredox-mCherry Expression in Arabidopsis.
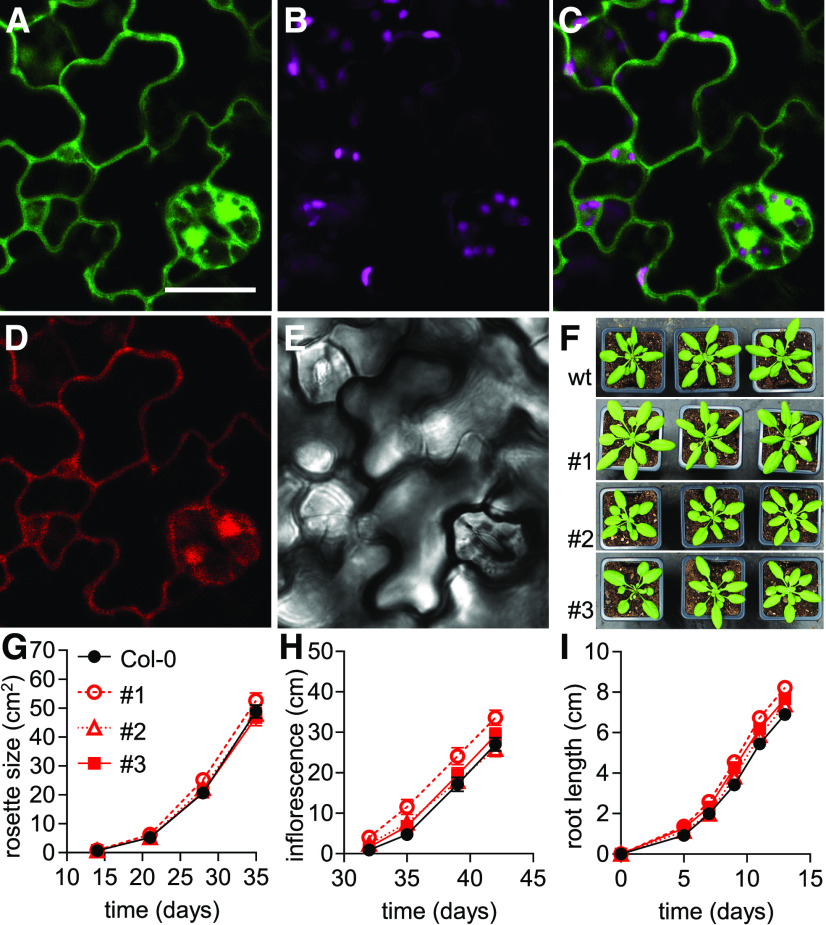
(A) to (F) Subcellular localization of Peredox-mCherry in abaxial epidermal cells of cotyledons of 5-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings. (A) tS fluorescence (green): excitation, 405 nm; emission, 517.5 ± 7.5 nm. Bar = 20 µm. (B) Chlorophyll fluorescence (magenta): excitation, 575 nm; emission, 675 ± 25 nm. (C) Overlay of tS and chlorophyll fluorescence. (D) mC fluorescence (red): excitation, 575 nm; emission, 612.5 ± 7.5 nm. (E) Transmission of the tS channel. Six analogous cotyledon epidermal areas were assessed in each of four seedlings. Consistent localization was observed in all three Peredox-mCherry lines. (F) Representative phenotypes of 28-d-old Arabidopsis plants of three independent homozygous biosensor lines (#1, #2, and #3) grown side by side with wild-type (wt) control (Col-0) plants in soil under long-day conditions.
(G) Rosette leaf area of the three sensor lines compared to Col-0 quantified across the plant growth period in soil (n = 19 to 20, means ± se).
(H) Inflorescence height of the plants (n = 19 to 20, means ± se).
(I) Vertical primary root length on half-strength MS medium supplemented with 1% (w/v) Suc and 1% (w/v) agar (n = 25, means ± se). Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test for data in (G) to (I). Note that line #1 showed significantly increased inflorescence height and root length (P < 0.001) compared to Col-0; rosette size of line #1 and all comparisons of lines #2 and #3 were not significantly different from the Col-0 control (P > 0.05; Supplemental Data Sets 1A to 1C).