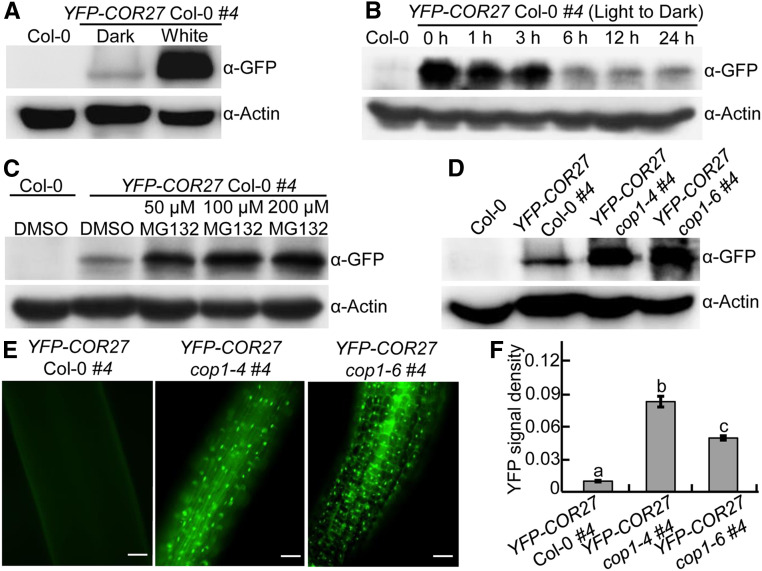
Figure 2.
COP1 Promotes the Degradation of COR27 in the Dark.
(A) YFP-COR27 protein levels in 4-d-old YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4 transgenic seedlings grown in the dark or constant white light conditions, as determined by immunoblot analysis. Col-0 served as a negative control. Actin was used as a loading control.
(B) Immunoblot detection of YFP-COR27 in YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4 transgenic seedlings grown in white light for 4 d and then transferred to darkness for various time intervals. Col-0 served as a negative control. Actin was used as a loading control.
(C) YFP-COR27 protein levels in 4-d-old dark-grown YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4 transgenic seedlings treated with various MG132 concentrations (0, 50, 100, and 200 μM). Col-0 treated with DMSO served as a negative control. Actin was used as a loading control.
(D) YFP-COR27 protein levels in YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4, YFP-COR27 cop1-4 #4, and YFP-COR27 cop1-6 #4 grown in the dark for 4 d. Col-0 served as a negative control. Actin was used as a loading control.
(E) Analysis of YFP-COR27 in hypocotyls by fluorescence microscopy. YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4, YFP-COR27 cop1-4 #4, and YFP-COR27 cop1-6 #4 seedlings were grown in the dark for 4 d. Bar = 10 μm.
(F) Relative YFP fluorescence intensity in hypocotyls from YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4 and YFP-COR27 cop1-4 #4 and YFP-COR27 cop1-6 #4 transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. The data represent means ± sd (n = 30) of three biological replicates. Letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis.