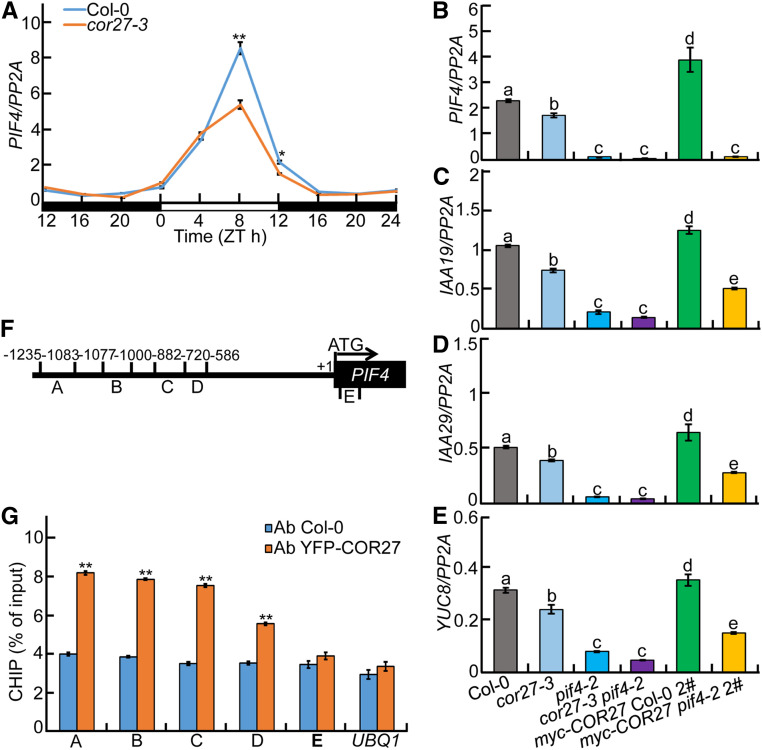
Figure 8.
COR27 Binds to PIF4 Promoter Regions and Upregulates Transcription of PIF4 and Its Targets.
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of rhythmic PIF4 transcript levels in Col-0 and cor27-3 mutant seedlings grown in 12-h-light/12-h-dark cycles for 5 d. Three biological replicates, each with three technical repeats, were performed. The data represent means ± sd of three biological repeats. Asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01), as determined by Student’s t test.
(B) to (E) RT-qPCR analysis of PIF4 (B) and PIF4 target genes (IAA19, [C]; IAA29, [D]; YUC8, [E]) expression in Col-0, cor27-3, pif4-2, cor27-3 pif4-2, myc-COR27 Col-0 #2, and myc-COR27 pif4-2 #2 seedlings. Seedlings of the indicated genotypes were grown in 12-h-light/12-h-dark cycles for 5 d. Samples were collected at ZT8 for total RNA extraction. Three biological replicates, each with three technical repeats, were performed. The data represent means ± sd of three biological repeats. Letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis.
(F) Illustration of PIF4 promoter regions with the indicated positions of primers used in ChIP-qPCR experiments.
(G) ChIP-qPCR assays showing that COR27 associates with the PIF4 promoter in vivo. ChIP-qPCR assays were performed using 5-d-old Col-0 and YFP-COR27 Col-0 #4 seedlings with anti-GFP antibodies. Plants were grown in 12-h-light/12-h-dark cycles and harvested at ZT8. The data represent means ± sd of three biological repeats. Asterisks indicate significant differences (**P < 0.01), as determined by Student’s t test.