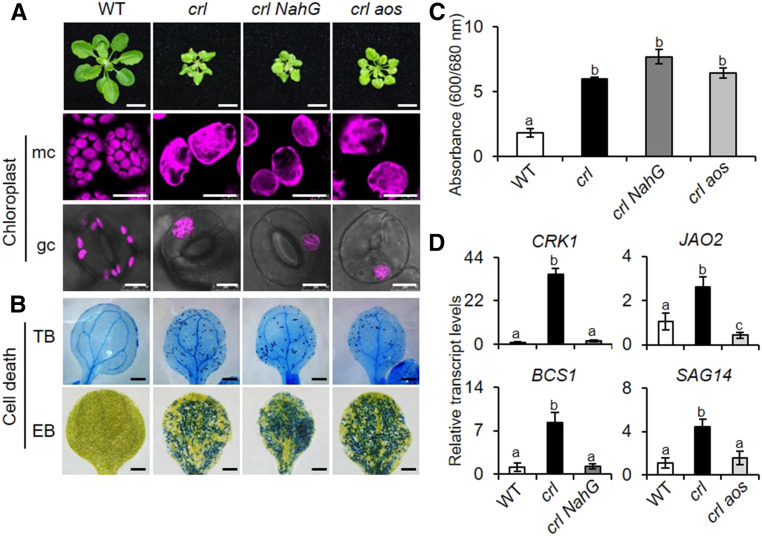
Figure 3.
SA- and JA-Independent Cell Death in crl.
(A) Macro- and microscopic phenotypes of the wild type (WT), crl, crl NahG, and crl aos. Images are representative of 21-d-old plants grown on soil under CL (bars in top row = 1 cm). Representative confocal images of chlorophyll autofluorescence in mesophyll cells (mc) and guard cells (gc) in 5-d-old seedlings grown on MS medium under CL (bars in middle and bottom rows = 20 μm for mc and 8 μm for gc).
(B) Cell death was visualized by TB and EB staining in the cotyledons of 10-d-old seedlings. Bars = 0.1 cm. WT, wild type.
(C) Dead cells visualized by EB in (B) were quantified by measuring relative EB absorbance as A600/A680. For EB staining, quantification was done using five cotyledons per genotype. Experiments were repeated at least three times, and the data represent means ± sd (Supplemental File). WT, wild type.
(D) Relative transcript levels of SA-responsive genes (CRK1, BSC1) and JA-responsive genes (JAO2, SAG14). Gene expression was determined in 5-d-old seedlings using RT-qPCR. ACT2 was used as an internal standard. Value represents means ± sd of three independent biological replicates. In (B) and (D), lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences between mean values at each genotype (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc honestly significant difference (HSD) test; Supplemental File). WT, wild type.