Figure 5.
Inactivation of FAD5 Abrogates Cell Death in crl.
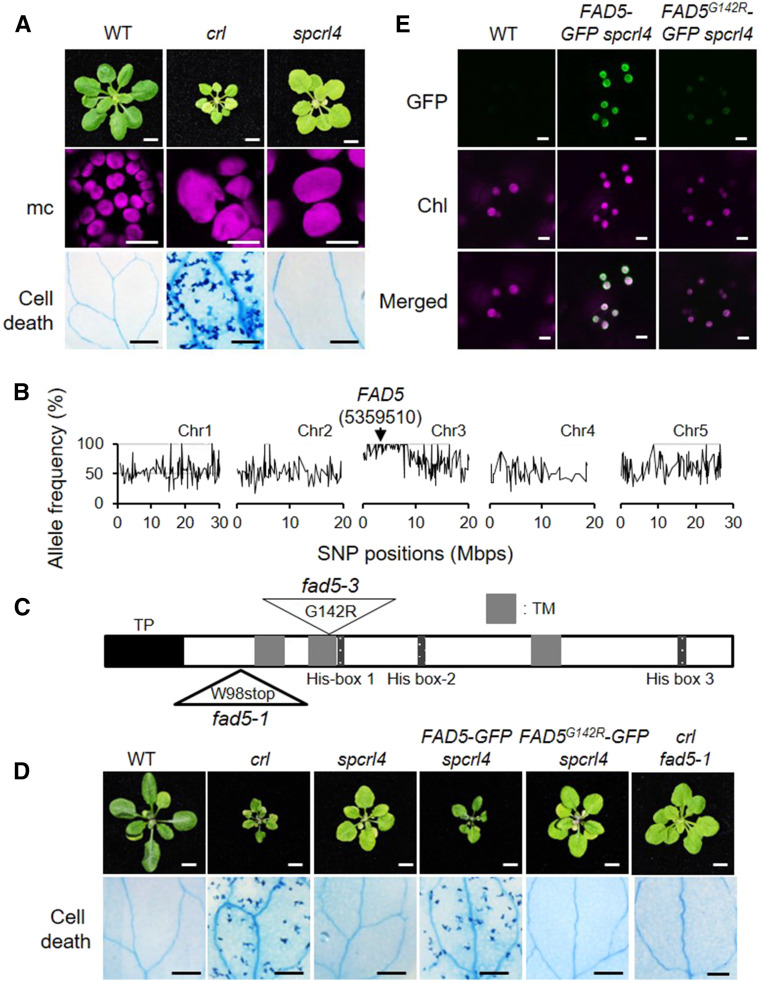
(A) Representative images of 21-d-old plants grown on soil under CL are shown in the top row. Bars = 0.5 cm. Confocal images of chlorophyll fluorescence in mesophyll cells (mc) in 5-d-old seedlings are shown in the middle row. Bars = 15 µm. Cell death in cotyledons (10-d-old seedlings) was visualized by TB staining, and representative results are shown in the bottom row. Bars = 1 mm. WT, wild type.
(B) Whole-genome sequencing of spcrl4 in comparison with crl identified a mutation in FAD5 at position 5359510 in chromosome (Chr) 3. Mbps, million base pairs.
(C) Schematic illustration of FAD5 shows a transit peptide (TP, black), three transmembrane domains (TM, gray), and three His-box domains (dark gray). The mutation positions for fad5-1 and fad5-3 are indicated with triangles. G, Gly; R, Arg; stop, stop codon; W, Trp.
(D) Complementation assay. Images are representative of 21-d-old plants grown on soil under CL and shown at the same scale. Bars in top row = 0.5 cm. Cell death was visualized by TB staining in the cotyledons of 10-d-old seedlings grown under CL, and a representative image from each genotype is shown. Bars in bottom row = 1 mm. WT, wild type.
(E) Subcellular localization of FAD5-GFP and FAD5G142R in 5-d-old seedlings of stable spcrl4 transgenic lines grown on soil under CL. Bars = 5 μm. Chl, chlorophyll autofluorescence; WT, wild type.