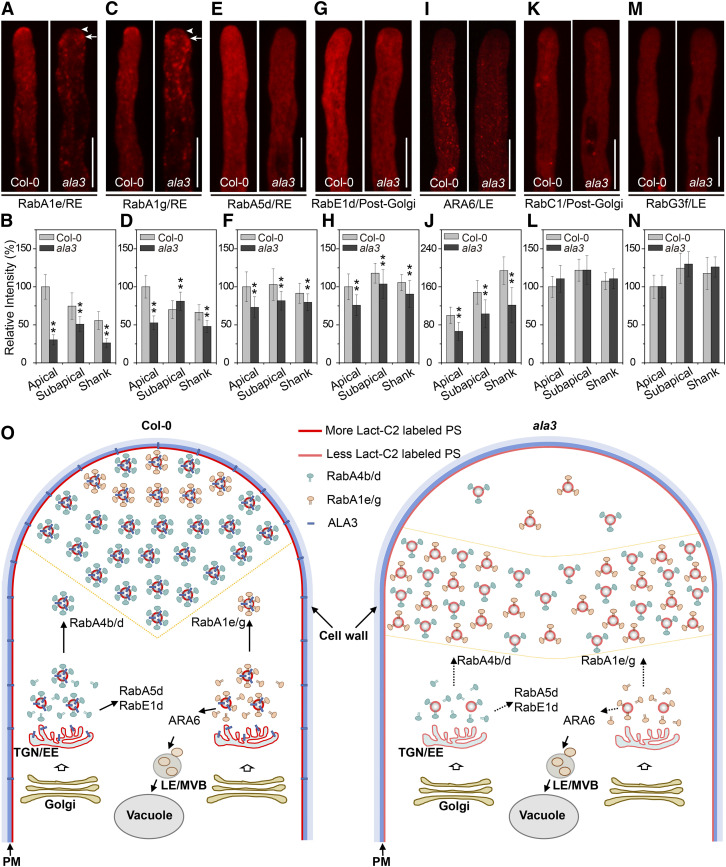
Figure 7.
The Localization and Distribution of Secreted Rab GTPases in the Pollen Tube Are Changed in ala3.
(A), (C), (E), (G), (I), (K), (M) Representative confocal images of growing pollen tubes from Col-0 and ala3-expressing mCherry-RabA1e (RE) (A), mCherry-RabA1g (RE) (C), mCherry-RabA5d (RE) (E), mCherry-RabE1d (post-Golgi) (G), RFP-ARA6 (LE) (I), mCherry-RabC1 (post-Golgi) (K), or mCherry-RabG3f (LE) (M) from the same transgene. The arrowhead and arrow indicate the apical and subapical zones, respectively. Bars = 10 μm.
(B), (D), (F), (H), (J), (L), (N) Quantitative analysis of the relative fluorescence intensity of mCherry-RabA1e (RE) (B), mCherry-RabA1g (RE) (D), mCherry-RabA5d (RE) (F), mCherry-RabE1d (post-Golgi) (H), RFP-ARA6 (LE) (J), mCherry-RabC1 (post-Golgi) (L), and mCherry-RabG3f (LE) (N) in Col-0 and ala3 pollen tubes. The results represent the means ± sds (n = 30). **P < 0.01 (t test compared to wild-type values).
(O) A model was proposed for the role of ALA3 in the polarized distribution of PS and vesicle trafficking. In Col-0 pollen tubes, ALA3 is required for the polarized distribution of PS, which regulates the distribution and activity of certain Rab GTPases. In ala3 pollen tubes, the total PS level at the cytosolic leaflet decreases significantly, and PS accumulates in the subapical zone, causing reduced vesicle formation and accumulation of vesicles in the subapical zone. The mislocalization of vesicles causes failed secretion, leading to pollen tube growth defects.