Figure 1.
Detection and Characterization of the C2N Short Transcript.
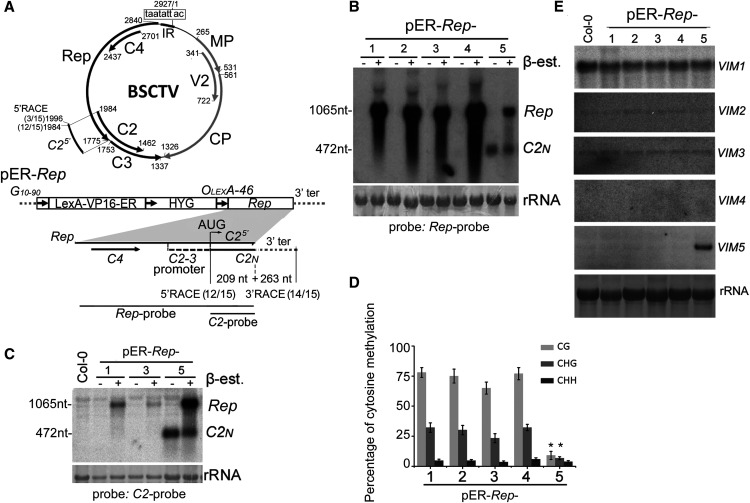
(A) Schematic diagram of the monopartite geminivirus BSCTV genome (top). BSCTV contains an IR with an invariant nonanucleotide (boxed) to direct the bidirectional transcription of viral mRNAs encoding Rep (also known as C1), C4, C2, and C3 from the complementary strand and CP (or V1), V2, and MP (or V3) from the virion strand, which are shown as thick arrows with the nucleotide positions indicated. The inducible transgene construct pER-Rep (bottom) consists of a strong synthetic constitutive promoter (G10-90); a chimeric transactivator (LexA-VP16-ER) containing the regulatory domain of an estrogen receptor (Zuo et al., 2000); a hygromycin-resistance marker (HYG); eight copies of the LexA DNA binding site fused to the -46 cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter (OLexA-46); and the Rep coding sequence of BSCTV, which also encodes the full-length C4, the C2-3 promoter, and a portion of the C2 in overlapping reading frame, C25′. C2N, a short C2 transcript of 472 nucleotides (nt; 209 nt C25′ + 263 nt 3′ terminal [ter] from vector) detected by 5′ and 3′ RACE. The total number of transcripts and the number sequenced from pER-Rep-5 plants at the indicated sites are shown in brackets.
(B) and (C) Detection of Rep mRNA (1065 nucleotides [nt]) and C2N (472 nt) from pER-Rep plants and Col-0. Total RNA was extracted from the rosette leaves of 2-week-old seedlings of different pER-Rep transgenic lines (60 individual seedlings per line) that were grown on MS medium with hygromycin, transferred onto MS medium with (+) or without (–) β-estradiol (β-est) for 16 h of induction, and analyzed by RNA blotting using a DNA probe specific to Rep (B) or C2 fragment (C). rRNA was stained by methylene blue as a loading control.
(D) Analysis of DNA methylation in the C2-3 promoter pER-Rep lines by bisulfite sequencing analysis. Samples were collected as described in (C). The original data are shown in Supplemental Figure 1. The statistical analysis was performed using OriginPro 8 (http://www.originlab.com). Values are means ± se, and asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in pER-Rep-5 compared with the other lines (n = 20; one-way ANOVA, P < 0.05).
(E) Detection of the expression of VIM family genes by RNA gel blotting. Rosette leaves of the 4-week-old wild-type Col-0 and transgenic pER-Rep plants were harvested for RNA isolation. VIM5 was highly induced in the pER-Rep-5 line.
Note that the seedlings analyzed in (B) were from the T2 generation, and the seedlings in (C) to (E) were the respective pER-Rep transgenic plants from the T6 generation.