Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2-Reactive CD4-CTLs and Single-Cell TCR Sequence Analysis
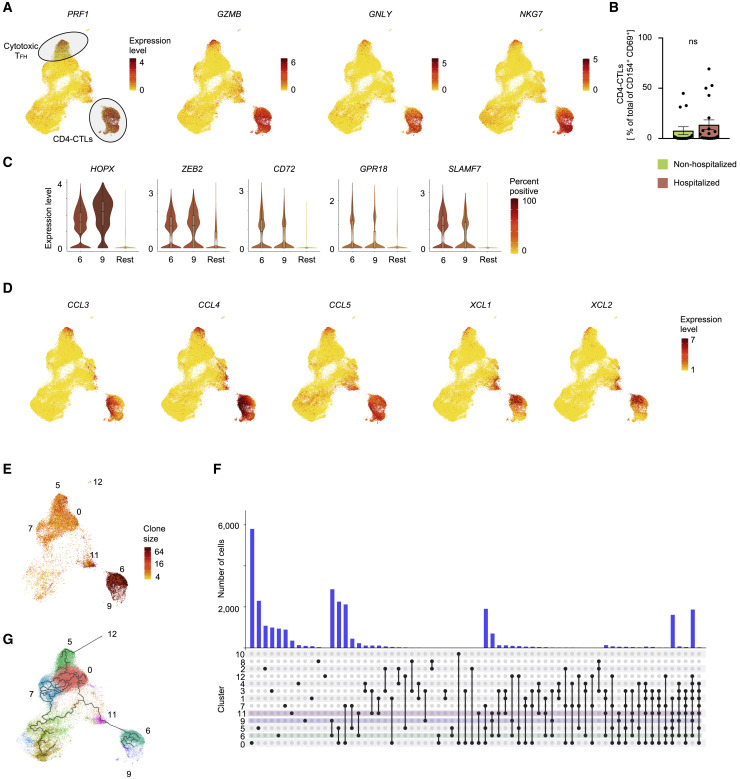
(A) UMAPs showing Seurat-normalized expression level of PRF1, GZMB, GNLY, and NKG7 transcripts in each virus-reactive cell.
(B) Percentage of CD4-CTLs (clusters 6 and 9) in the total SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4+ T cell pool for non-hospitalized and hospitalized COVID-19 patients; dots indicate data from a single subject. Data are mean ± SEM; significance for comparisons was computed using Mann-Whitney U test; ns, non-significant P value..
(C) Violin plots showing normalized expression level (log2(CPM+1)) of transcription factors HOPX and ZEB2 and effector molecules CD72, GPR18, and SLAMF7 transcripts in virus-reactive cells from designated clusters (6 and 9) compared to an aggregation of remaining cells (Rest).
(D) UMAPs showing Seurat-normalized expression of CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, XCL1, and XCL2 transcripts in each virus-reactive cell.
(E) UMAP showing TCR clone size (log2, color scale) of SARS-CoV-2-reactive cells from COVID-19 patients (6 h stimulation condition).
(F) Histogram bar graph (top) displaying single-cell TCR sequence analysis of SARS-CoV-2-reactive cells. Each bar shows the number of TCRs shared between cells from individual clusters (rows, connected by lines). Connected lines (bottom) indicates what clusters are sharing TCRs. Clusters 6 (green), 9 (blue), and 11 (pink), i.e., CD4-CTLs, are highlighted.
(G) Single-cell trajectory analysis showing relationship between cells in different clusters (line), constructed using Monocle 3. Only SARS-CoV-2-reactive cells from COVID-19 patients (6 h stimulation condition) are shown.