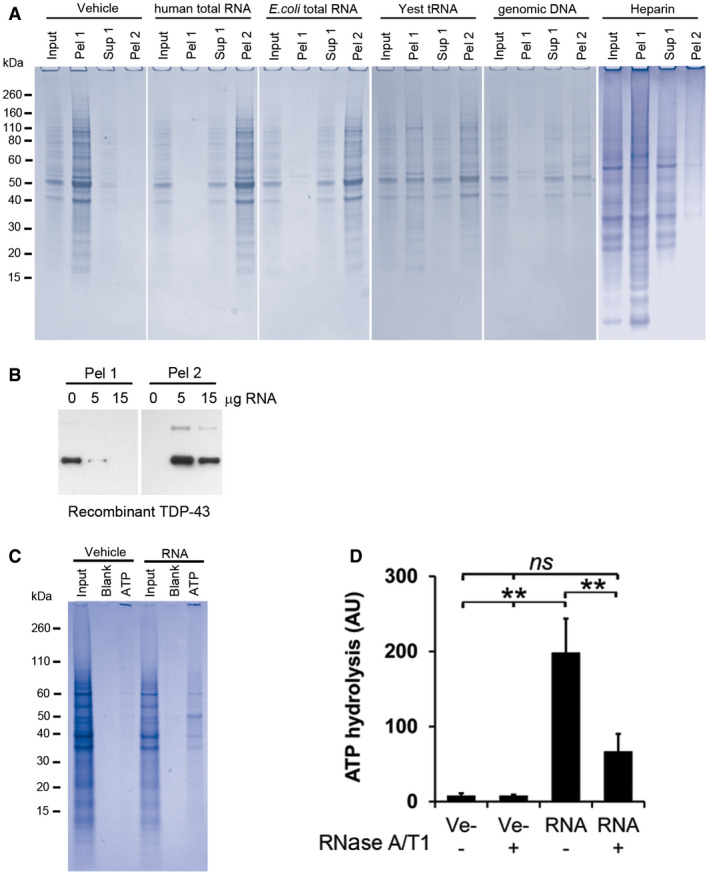
Figure EV4. Protein renaturation: effects on enzymatic activity and effects of various polyanions.
-
ACoomassie‐stained SDS‐PAGE gels of RNase‐aggregated proteins from human neurons renatured with various polyanions. Input represents 1/10th of each sample, taken before the first centrifugation, and Pel 1 and Sup 1 are the pellet and the supernatant, respectively, recovered after the first centrifugation. Pel 2 represents the pellet obtained after treating the Sup 1 fraction with RNase A/T1 followed by centrifugation. See experimental outline in Fig 3A for a full description.
-
BRenaturing of recombinant TDP‐43 using increasing amounts of total RNA. Pel 1 represents aggregated protein after renaturing. Pel 2 is the aggregated protein after the soluble fraction (Sup 1) has been treated with RNase A/T1.
-
CGel electrophoresis analysis of proteins from human neurons renatured with vehicle or total RNA and then captured with ATP‐agarose beads (ATP). Input represents 1/10th of each sample taken directly after renaturation, before the first centrifugation, and Blank represents the sample without any ATP‐agarose beads present.
-
DATP‐hydrolysing activity of RNase‐aggregated proteins from Jurkat T cells renatured in the presence (RNA) or absence (Ve−) of RNA.
