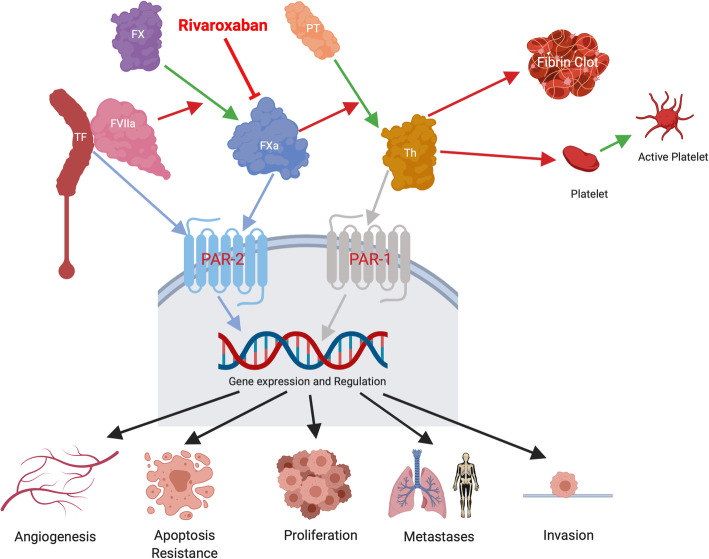
Fig. 1.
The extrinsic coagulation pathway. Tissue Factor (TF), the main initiator of the coagulation cascade, complexes with Factor VIIa to activate Factor X, and in turn converts prothrombin (PT) to thrombin (Th) and ultimately fibrinogen to fibrin, with subsequent clot formation. FXa is inhibited by the direct oral anticoagulant Rivaroxaban. Thrombin also binds to protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1), and the TF/FVIIa/Xa complex to PAR-2. In cancer cells, this is proposed to result in pro-angiogenic, pro-proliferative and pro-invasive gene expression resulting in increased metastases. Figure created with BioRender.com [6]. Abbreviations: TF, Tissue Factor; FVIIa, activated Factor VII; FX, Factor X; FXa, activated Factor X; PT, prothrombin; Th, thrombin; PAR, protease-activated receptor