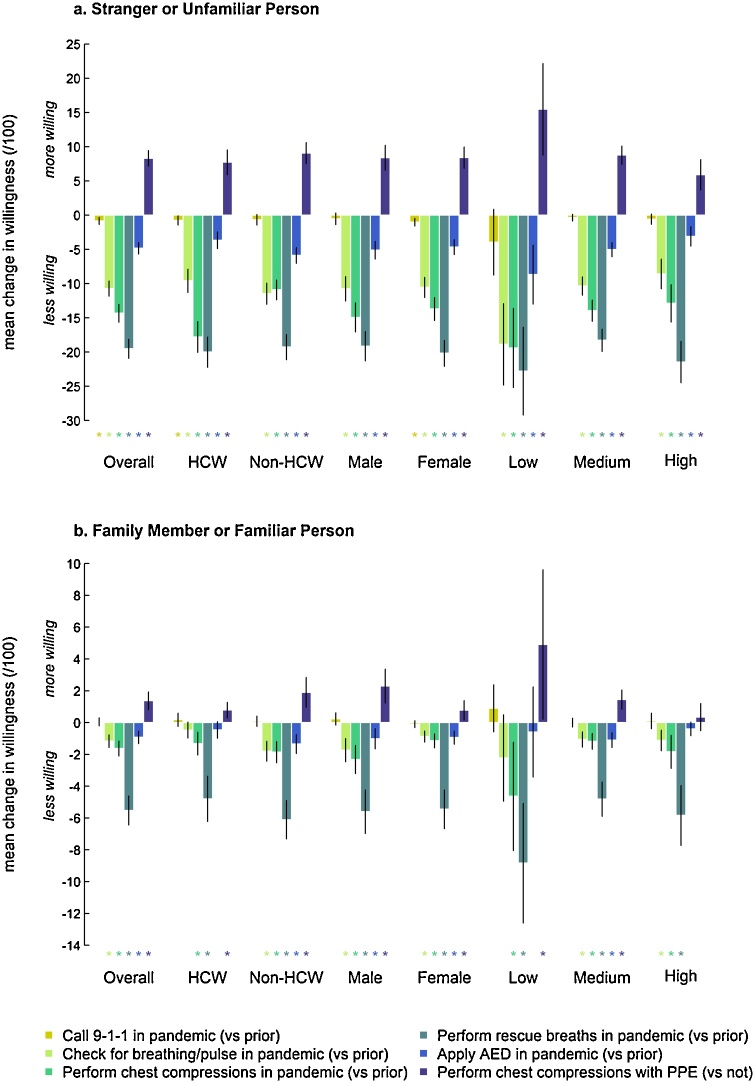
Fig. 1.
Change in bystander willingness to intervene in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests during the COVID-19 pandemic, for (1a) strangers or unfamiliar persons and (1b) family or familiar persons, overall and among subgroups. Subgroups include: (1) healthcare and non-healthcare workers; (2) female and male; (3) per capita COVID-19 incidence in the country or province/state (if in North America) of the participant (grouped as “Low” [0–50], “Medium” (50–200], or “High” [>200 cases per 100,000 people10]; the right endpoints are included in the group). Each bar represents the mean change in willingness (with 95% confidence intervals), calculated with paired t-tests, to perform the specified intervention. * Denotes a p value <0.05. HCW, healthcare worker; PPE, personal protective equipment (including a face-mask for the rescuer and the victim, and gloves for the rescuer); AED, automated external defibrillator.