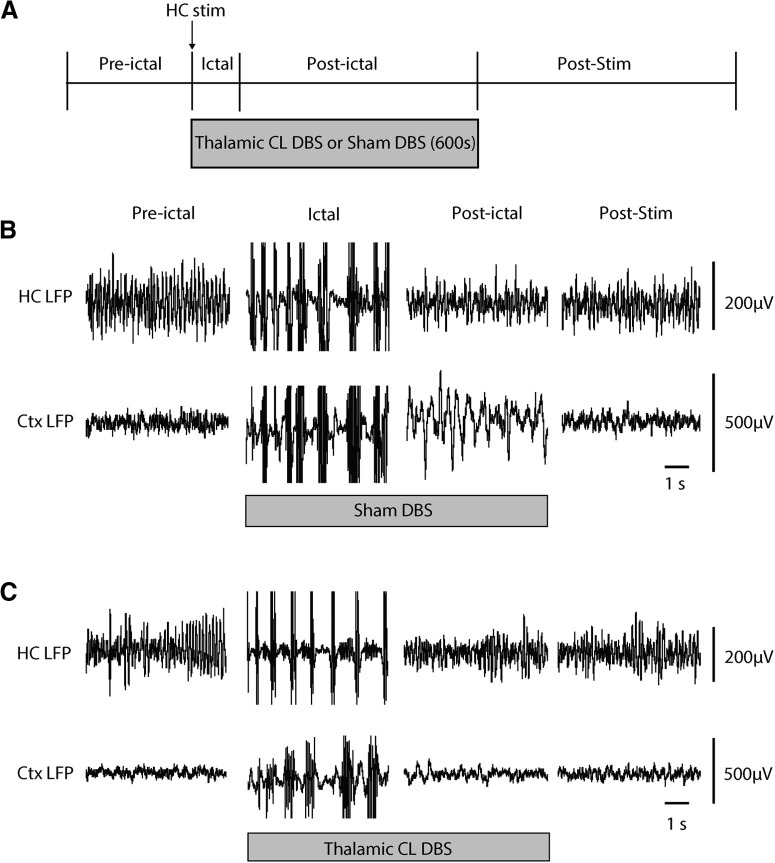
Figure 2.
Thalamic CL DBS produces cortical physiological arousal in the postictal period during the sucrose reward spontaneous licking task. A, Experimental protocol and sequence of preictal, ictal, postictal, and poststimulation (post-stim) epochs. HC stimulation for 2 s at 60 Hz induces a secondarily generalized seizure. Simultaneous with seizure onset, bilateral thalamic CL DBS or sham control DBS is initiated and continued for 5 min (600 s) total, typically spanning both the ictal and postictal periods. B, Recordings during sham DBS. Preictal, ictal, postictal, and post-stim time samples exemplify secondarily generalized seizures evidenced by polyspike discharges in both HC and orbital frontal Ctx LFP during the ictal period; prominent slow waves in Ctx LFP during the postictal period; and recovery in the post-stim period. C, Recordings during therapeutic thalamic CL DBS (100 Hz, 100-µA split approximately equally between the two thalami). Thalamic CL DBS markedly decreases postictal slow wave activity in Ctx compared with sham control (B). Ctx, orbital frontal cortex.