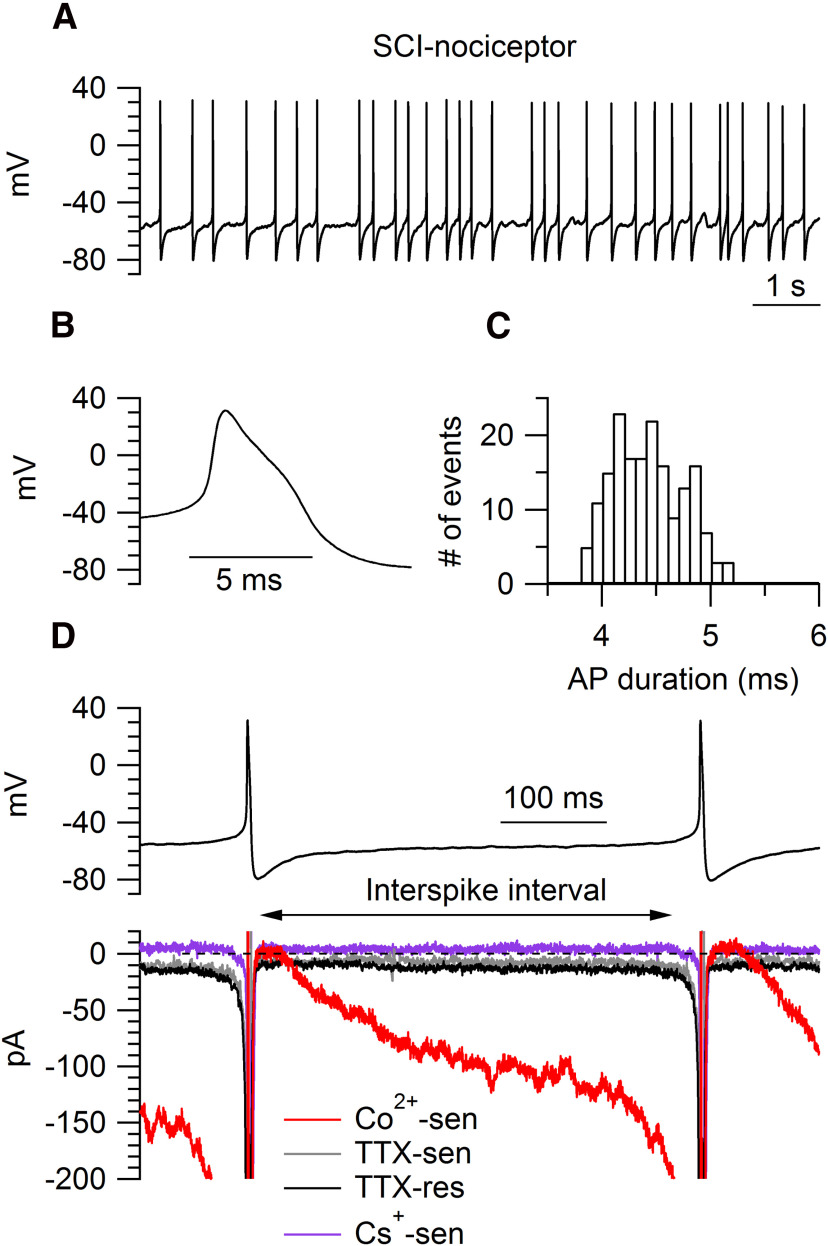
Figure 2.
Interspike currents isolated with the action potential-clamp technique in SCI-nociceptors. A, Spontaneous activity recorded in current clamp from a SCI-nociceptor in vitro. B, Representative action potential from the cell in A showing a characteristic shoulder during the repolarization phase and a long duration (4.2 ms, measured at half-maximal amplitude). C, Histogram of the action potential duration (measured at half-maximal amplitude) for the cell in A during 1 min of recording. D, top panel, Action potentials recorded in current clamp from a spontaneously active SCI-nociceptor were used as voltage command in voltage clamp. Bottom panel, Representative interspike currents. Here and in the following figures, interspike currents were isolated by subtracting traces (average of three consecutive traces) before and after application of a specific blocker. Total calcium current (Co2+-sen, red trace) isolated as the current sensitive to replacement of 2 mm Ca2+ with 2 mm Co2+ in the external solution; TTX-sensitive sodium current (TTX-sen, gray trace) isolated as the current sensitive to 1 μm TTX; TTX-resistant sodium current (TTX-res, black trace) isolated as the current sensitive to 1 μm A803467 applied on top of 1 μm TTX; Ih current (Cs+-sen, purple trace) isolated as the current sensitive to 3 mm Cs+.