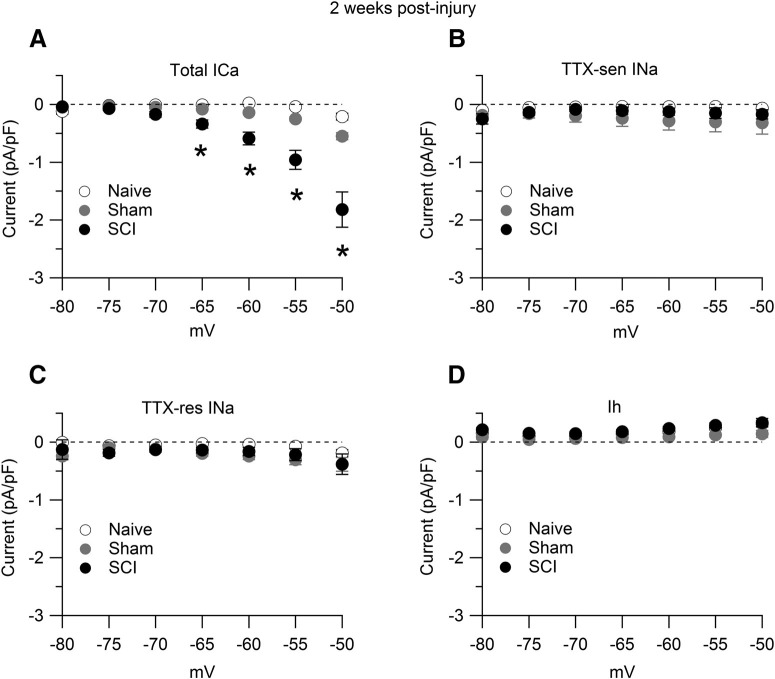
Figure 3.
Interspike calcium, sodium, and Ih currents. Interspike currents were measured in SCI-nociceptors and sham-nociceptors isolated at 15 d postinjury and postlaminectomy, respectively, and in age-matched naive-nociceptors. A, Total interspike calcium current isolated as the current sensitive to replacement of 2 mm Ca2+ with 2 mm Co2+ in the external solution in naive-nociceptors (white dots, n = 16), sham-nociceptors (gray dots, n = 15), and SCI-nociceptors (black dots, n = 17). B, Interspike TTX-sensitive (TTX-sen) sodium current isolated as the current sensitive to 1 μm TTX in naive-nociceptors (white dots, n = 13), sham-nociceptors (gray dots, n = 17), and SCI-nociceptors (black dots, n = 18). C, Interspike TTX-resistant (TTX-res) sodium current isolated as the current sensitive to 1 μm A803467 applied on top of 1 μm TTX in naive-nociceptors (white dots, n = 13), sham-nociceptors (gray dots, n = 17), and SCI-nociceptors (black dots, n = 18). D, Interspike Ih current isolated as the current sensitive to 3 mm Cs+ in naive-nociceptors (white dots, n = 12), sham-nociceptors (gray dots, n = 17), and SCI-nociceptors (black dots, n = 20). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc comparison test. A, At –65 mV: sham versus naive, p = 0.69; SCI versus naive, *p < 0.05; SCI versus sham, *p < 0.05. At –50 mV: sham versus naive, p = 0.48; SCI versus naive, *p < 0.05; SCI versus sham, *p < 0.05. Data are reported as mean ± SEM.