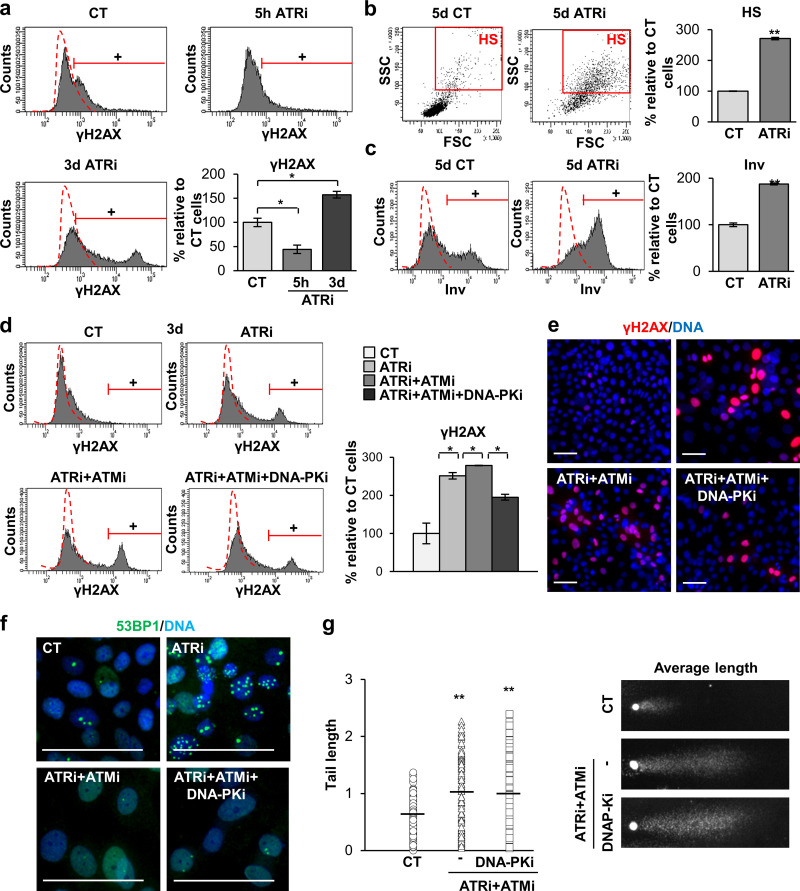
Figure 5.
Inhibition of the three DDR kinases impairs γH2AX signaling and causes accumulation of DNA damage in human keratinocytes. (a) Detection of γH2AX signal in cells treated with the DMSO vehicle as control (CT) or with ATRi for 5 h or 3 d as indicated, as measured by FC (+, positive cells according to negative isotype antibody control: red broken line). Bar histogram represents the percentage of keratinocytes positive for γH2AX relative to CT. (b) Light scatter parameters of cells treated for 5 d, as indicated. Red box gates HS, quantitated in the bar histogram, relative to CT. (c) Expression of Inv in cells treated for 5 d, as indicated, by FC (+, positive cells as in a, quantitated in the bar histogram, relative to CT). (d) Detection of γH2AX signal in keratinocytes treated with DMSO as indicated (CT), ATRi, ATRi + ATMi, or ATRi + ATMi + DNA-PKi for 3 d, analyzed by FC (+, positive cells as in a, quantitated in the bar histogram, relative to CT). (e) Detection of γH2AX (red) by IF. Scale bar, 50 µm. (f) Detection of 53BP1 (green) by IF in cells treated as in a. Scale bar, 25 µm. Nuclear DNA by DAPI. (g) Left: Quantification of comet tail lengths, in pixels, n = 145 cells of seven fields per slide of keratinocytes treated for 5 d as indicated. Horizontal bars indicate tail length average. Right: Representative average nuclear comets. Data are mean ± SEM of duplicate (b–d and g) or triplicate (a) samples. Datasets were compared by an unpaired t test (two-sided). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Scale bar, 50 µm. See also Fig. S5. FSC, forward scatter; SSC, side scatter.