Figure 1.
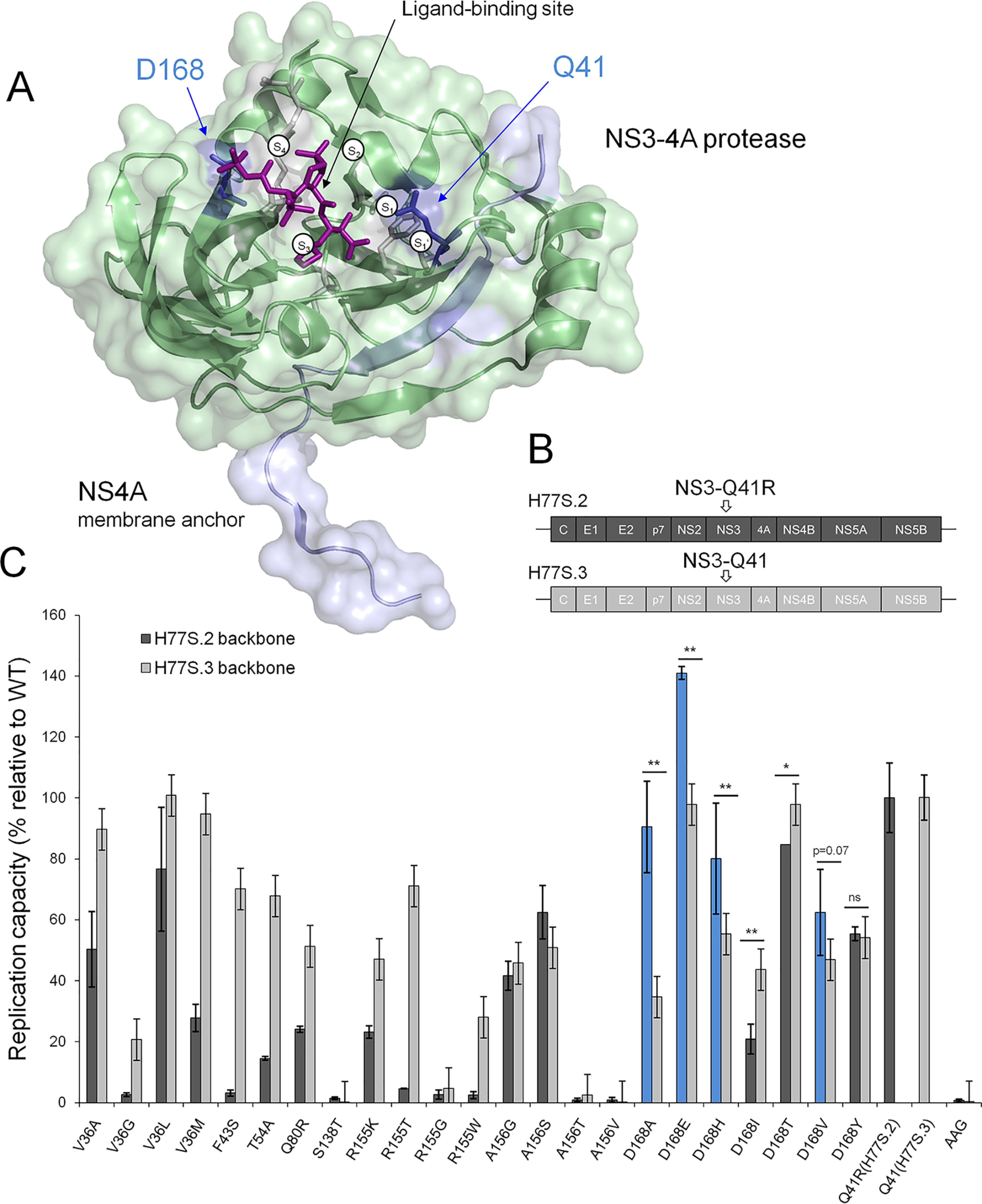
Replicative fitness of PI-resistant variants in NS3 ± Q41R protease genomic backgrounds. A, structural context of PI-resistance mutations depicted on the NS3-4A protease structure from PDB 2OC8 (50) with PI bound to the ligand-binding site (purple stick model); ligand-binding pockets S4 to S1′ (51). The protein surface is partially transparent; protease domain: green, NS4A: light blue. Gln41 and Asp168 are shown as blue stick models located at opposite ends of the protease substrate–binding pocket. B, the H77S.2 molecular clone contains six cell culture adaptive mutations (not shown) throughout the viral genome; the only cell culture adaptive mutation located in the NS3-4A protease domain, NS3-Q41R (depicted by arrow), is reverted back to NS3-Gln41 WT in H77S.3 (6). C, GLuc activity secreted by RNA-transfected cells normalized to pH77S.3 and pH77S.2 WT. Blue shading indicates PI-resistant variants with enhanced replicative fitness by NS3-Q41R. Data shown represent the mean ± S.D. from at least three independent experiments; *p < 0.001; **p < 0.0001; by two-sided t test. AAG, negative control.
