Figure 2.
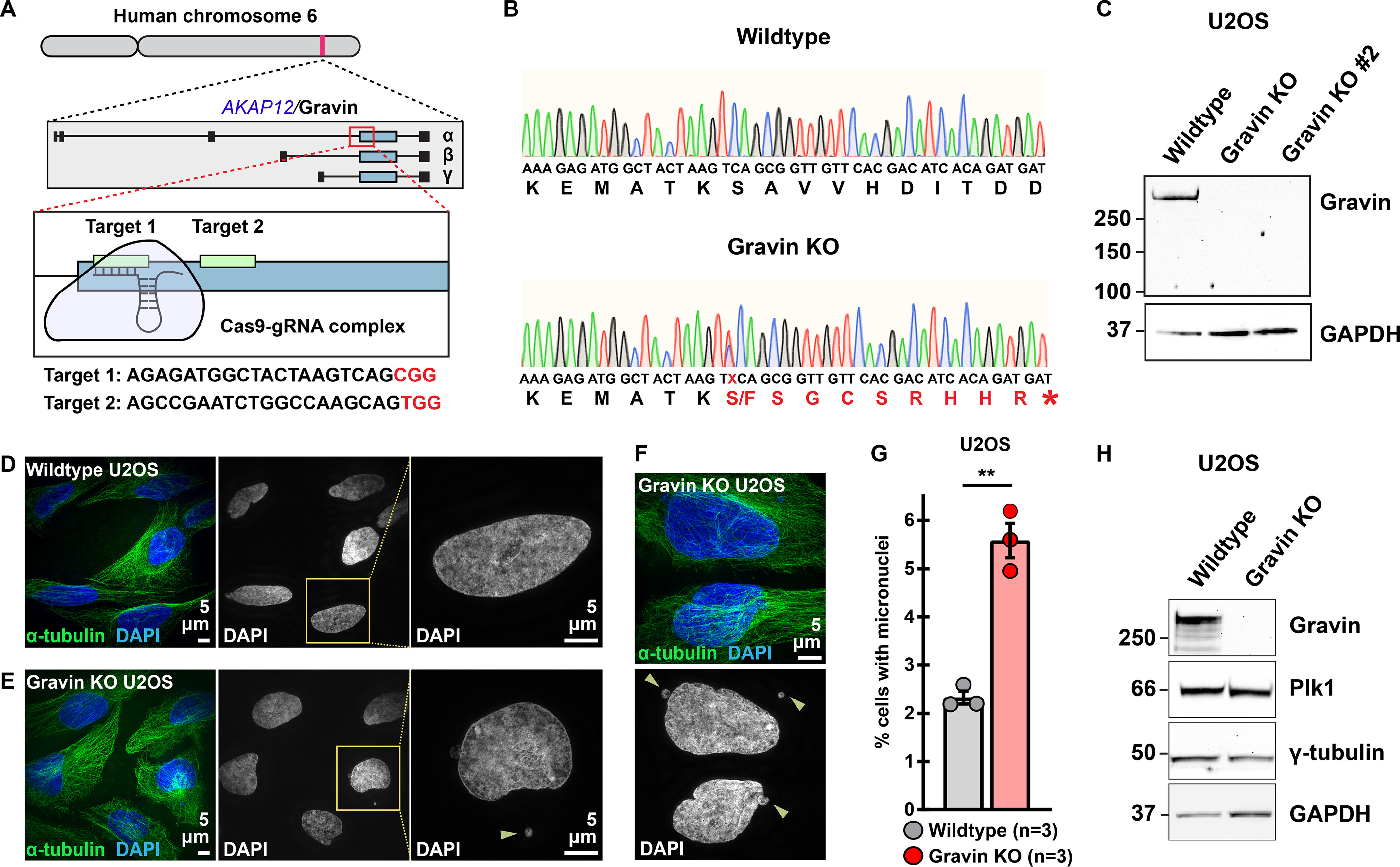
Generation of Gravin knockout U2OS cells. A, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of human chromosome 6 in U2OS cells to disrupt the Gravin-encoding gene, AKAP12 (top). Targets are directed to the exon that is shared by all three Gravin isoforms, α, β, and γ (middle). Two unique gRNAs were designed to targets 1 and 2 (bottom). Target sequences are presented below with protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sites highlighted in red. B, traces depicting nucleic (small letters) and amino (large letters) acid sequences for a representative WT (top) and Gravin KO (bottom) clone. A mutation present in Gravin KO cells alters the protein coding sequence (red) to generate a premature stop codon (*) and leads to a truncated protein. Traces represent pooled allele sequences for each individual clone. Two amino acid alterations were detected (S and F). C, immunoblot detection of Gravin (top) and GAPDH (bottom) in WT and Gravin KO clonal U2OS cells. D–F, SIM images of WT (D) and Gravin KO (E and F) cells during interphase. Composite images (left) show α-tubulin (green) and DAPI (blue). DAPI stain depicted in grayscale (middle). Magnified insets (right) and yellow arrows highlight micronuclei. G, quantification of amalgamated data representing the percent of cells with micronuclei in WT (gray) and Gravin KO (red) U2OS cells. Points depict individual experiments (n): WT, n = 3; Gravin KO, n = 3; **p = 0.001. A total of 1500 cells were analyzed over three independent experiments. P-values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. Data are mean ± S.E. H, immunoblot detection of Gravin (blot 1), Plk1 (blot 2), γ-tubulin (blot 3), and GAPDH (blot 4) in WT and Gravin KO U2OS cells.
