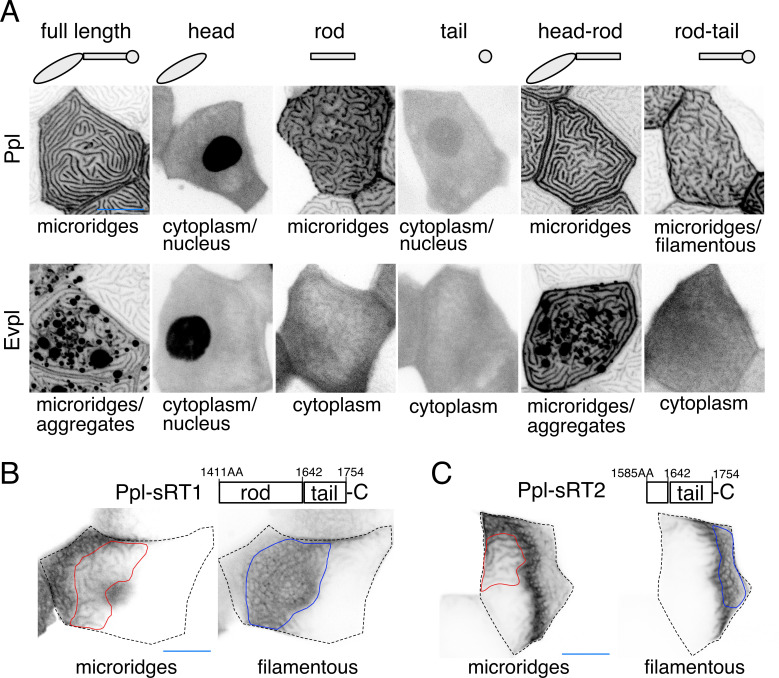
Figure 5. Ppl and Evpl domain localization.
(A) Periderm cells expressing Evpl-tdTomato and Ppl-GFP variants at 48hpf. Schematics indicate the domains in each variant. (B–C) Optical sections of GFP-tagged Ppl truncated rod-tail fusions expressed in periderm cells at 48hpf. Sections highlight the microridge-like pattern at the apical surface of cells (left, red outlines) or the filamentous pattern deeper in cells (right, blue outlines). Top: Diagram of Ppl protein domains. Amino acid numbers are indicated. See Figure 5—video 1 for video showing apical-to-basal sections of these images. Images were inverted so that high-intensity fluorescence appears black and low-intensity fluorescence is white. Scale bars: 10 µm.