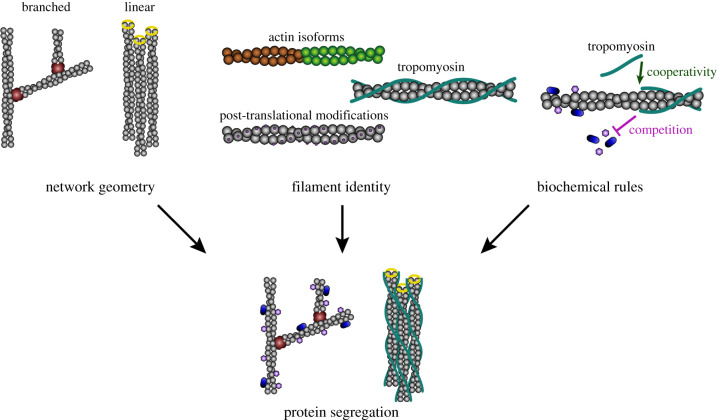
Figure 1.
Three main mechanisms that account for the segregation of ABPs to different actin networks in cells. Schematic of the different molecular mechanisms described in this review. Actin networks are distinguished by different geometries. For example, the Arp2/3 complex generates branched networks and formins generate linear arrays. Actin filaments have different molecular identities based on the use of various actin isoforms, post-translational modifications and/or the presence of tropomyosin. Additionally, ABPs can compete or cooperate to restrict or promote their binding to actin filaments.