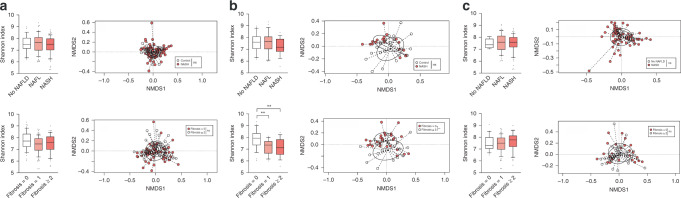
Fig. 1. Comparison of the diversity of gut microbial communities in all, non-obese, and obese subjects.
The alpha and beta diversity of a all (n = 202), b non-obese subjects (n = 64) (**P = 0.0074, F0 vs F1; **P = 0.0084, F0 vs F2–4), and c obese subjects (n = 138) divided by the histological spectra of NAFLD or fibrosis severity. Alpha diversity was based on the Shannon index with 12,000 rarefied sequences per sample. The box plots indicate the median, 25th to 75th percentiles (boxes), and 10th to 90th percentiles (whiskers). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-sided nonparametric Mann–Whitney test or a nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. NMDS plots were generated using relative OTU abundance data according to the Bray–Curtis distance, and statistical significance was measured using adonis analysis (panel b; *P = 0.038, F0 vs F2–4).