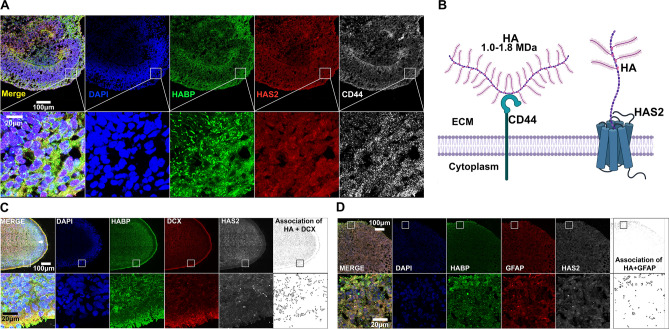
Figure 1.
Human IPSC-derived Cortical Spheroids Produce Hyaluronan ECM. (A) 10 μm thick cryosections of 90-day-old control spheroids were stained for ECM components. Left to right: merged channels, nuclei marker DAPI (blue), HA as detected by HABP (green), HA synthase HAS2 (red), and HA receptor CD44 (white). Bottom panel highlights a section of the cortical plate at increased magnification. Scale bar of top panel: 100 μm, bottom panel: 20 μm. (B) Graphic illustration of how HA is produced by HAS and interacts with CD44 at the cell membrane. (C) 10 μm thick cryosections of 90-day-old control spheroids were stained for DAPI (blue), HABP (green), neuronal marker DCX (red) and HAS2 (white). Arrows in top left panel highlight the cortical plate. Bottom panel highlights a section of the cortical plate at increased magnification. Scale bar of top panel: 100 μm, bottom panel: 20 μm. (D) 10 μm thick cryosections of 90-day-old control spheroids were stained for DAPI (blue), HABP (green), astrocyte marker GFAP (red) and HAS2 (white). Bottom panel highlights a section of the cortical plate at increased magnification. Scale bar of top panel: 100 μm, bottom panel: 20 μm. Further analysis of cell-type specific expression of HA-ECM components can be found in Fig. S2, while validation of HAS2 immunostaining can be found in Fig. S3.