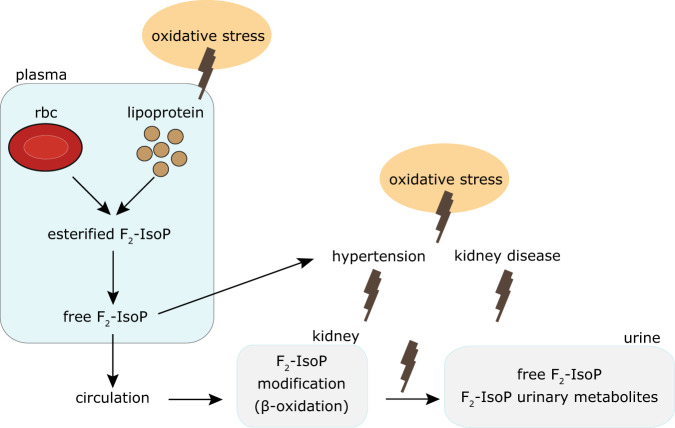
Fig. 9. Schematic representation of the conceptualized mechanism of oxidative stress.
Free F2-IsoP was formed from the esterified to phospholipids in RBCs and lipoprotein membranes in plasma. Free F2-isoP was then rapidly metabolized by the kidney and excreted in urine with its metabolites. Oxidative stress may affect the levels F2-IsoP directly but the downstream urinary F2-IsoP level may be modified indirectly by a series of events, including the kidney function, and hypertension.