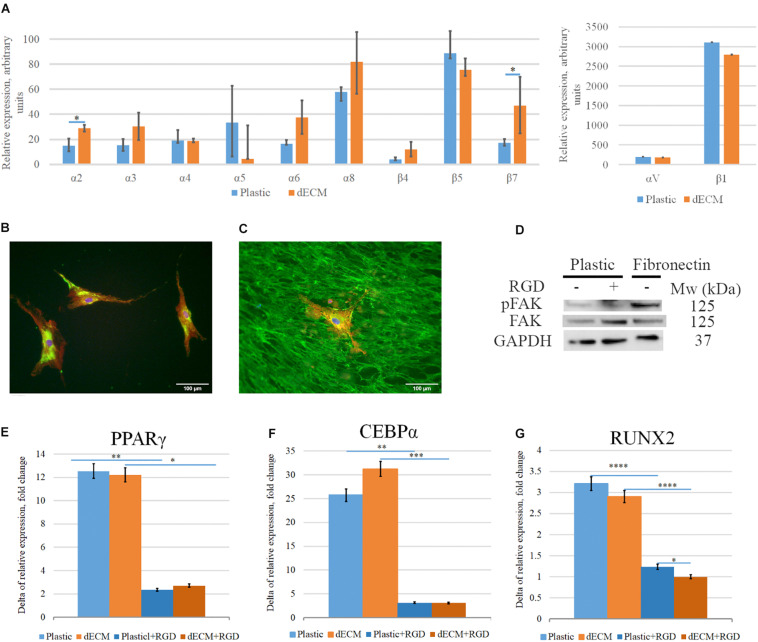
FIGURE 14.
Impact of interaction of hMSCs with dECM via integrins into dECM-mediated hMSCs differentiation stimulation. (A–C) Expression of integrins in hMSCs cultured on plastic (A,B) or dECM (A,C) estimated by real-time PCR (A) including α2(ITGA2), α3(ITGA3), α4(ITGA4), α5(ITGA5), αV(ITGAV), α6(ITGA6), α8(ITGA8), β1(ITGB1), β4(ITGB4), β5(ITGB5), β7(ITGB7) and immunocytochemical staining for integrin β1 subunit (B,C). (D) Activation of pFAK/FAK signaling pathway in hMSCs in suspension (1) on the presence of RGD peptide (2) or after 1-h attachment to fibronectin (3). (E–G) Relative fold change of hMSC differentiation induction (4 days) measured as increased expression of differentiation markers for adipogenic [PPARγ(PPARG) (E), CEBPα(CEBPA) (F)], and osteogenic [RUNX2 (G)] differentiation by real-time PCR normalized to housekeeping gene (RPLP0) in hMSCs cultured on plastic or dECM with or without blocking of integrin interaction via RGD sequence using RGD peptide. The quantitative data are represented as median (25%, 75%), ∗(p value < 0.05), ∗∗(p value < 0.005), ∗∗∗(p value < 0.0005), ****(p value < 0.0001).