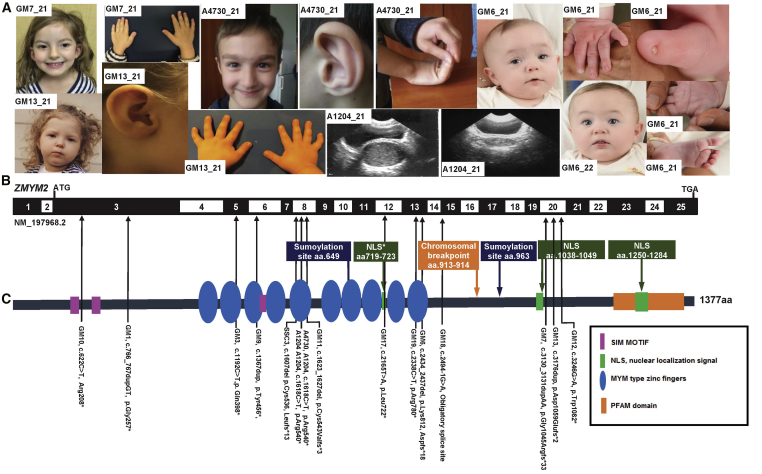
Figure 1.
Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies 14 Heterozygous Loss-of-Function Mutations in ZMYM2 in 15 Families with 19 Affected Individuals
(A) Clinical features of individuals with ZMYM2 mutations (see Table 1); family number is shown in the white rectangle.
Family GM7: Hypertelorism; simple helix and protuberant ears; 5th fingers and thumbs; 5th finger clinodactyly.
Family A4730: Wide eyebrows, mild synophrys, short filtrum; long nose with a bulbous tip; auricle with hypoplastic lobule; hyperextensibility of joints.
Family GM13: Wide interpupillary distance and intercanthal distance; small auricle; clinodactyly.
Family A1204: hematocolpos pre- and post-drainage.
Family GM6: (GM6_21) dysmorphic facial features with epicanthi, short 5th digit with hypoplastic nails, abnormal palmar crease and sandal gap toe; (GM6_22) Dysmorphic features – epicanthi.
(B) Exon structure of human ZMYM2 cDNA (GenBank: NM_197968.2) and positions of mutations (arrowheads).
(C) Protein domain structure of human Zmym2 showing the positions of each of the 14 different heterozygous mutations identified in 15 families (position indicated by the arrows shafts).
aa, amino acid; ATG, start codon; NLS, nuclear localization site.