Figure 3.
Array of CAKUT Phenotypes Observed in a Zmym2+/− Mutant Mouse Model
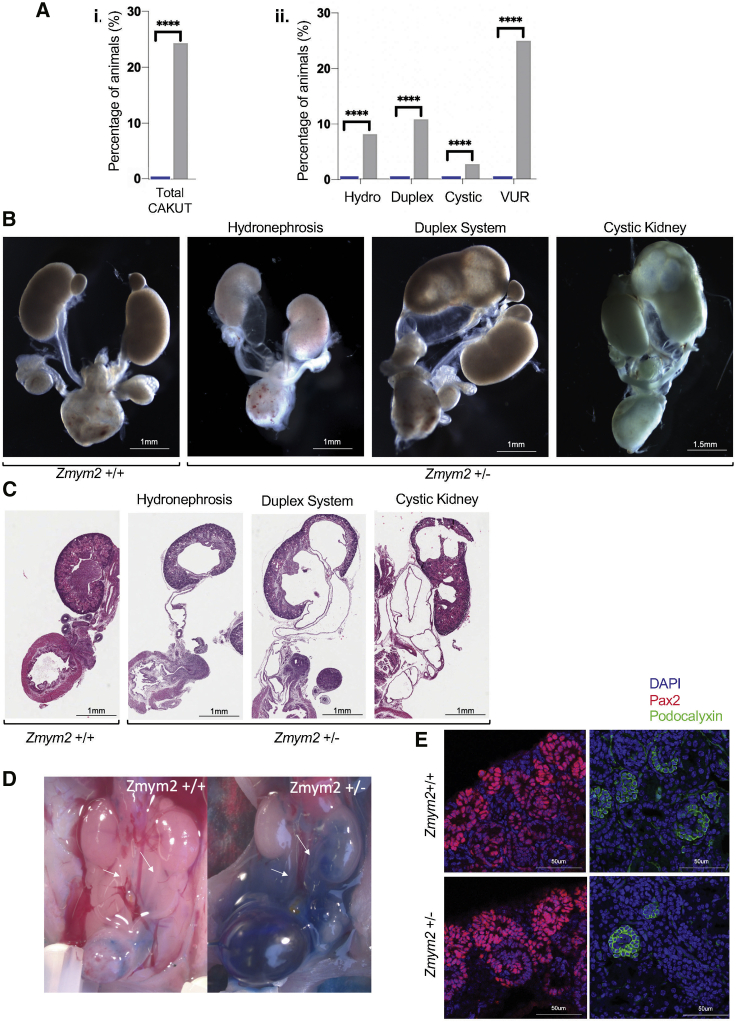
Zmym2+/− mice heterozygous for a frameshift mutation in exon 3 were analyzed at embryonic stage E18.5 and post-natal stage P0.
(A) Percentages of mice with given CAKUT phenotype observed in Zmym2+/− pups and their wild-type littermates. Statistical analysis was done using a binomial test. For CAKUT, hydroureter, duplex, and cystic kidneys phenotypes were compiled from Zmym2+/+ (n = 35) and Zmym2+/− (n = 37). Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) was assessed from Zmym2+/+ (n = 25) and Zmym2+/− (n = 20). Note, some animals harbored more than one CAKUT phenotype.
(B) Dissected E18.5 and P0 urogenital system of Zmym2+/+and Zmym2+/− mice demonstrating gross CAKUT phenotypes including hydroureter, hydronephrosis, duplex systems, and cystic kidneys, respectively.
(C) Haemotoxylin and Eosin staining of tissue sections derived from Zmym2+/+and Zmym2+/− urogenital systems.
(D) Intravesical dye injection showing vesicoureteral reflux in Zmym2+/+ and Zmym2+/− P0 mice.
(E) Immunohistofluorescence analysis of E18.5 kidneys reveals no overt difference in cap mesenchyme and ureter tips (Pax2) nor in podocytes (podocalyxin) between Zmym2+/+and Zmym2+/− kidneys.