Extended data 7 -. LbNOX improves hepatic insulin resistance in vivo independent of hepatic insulin signaling.
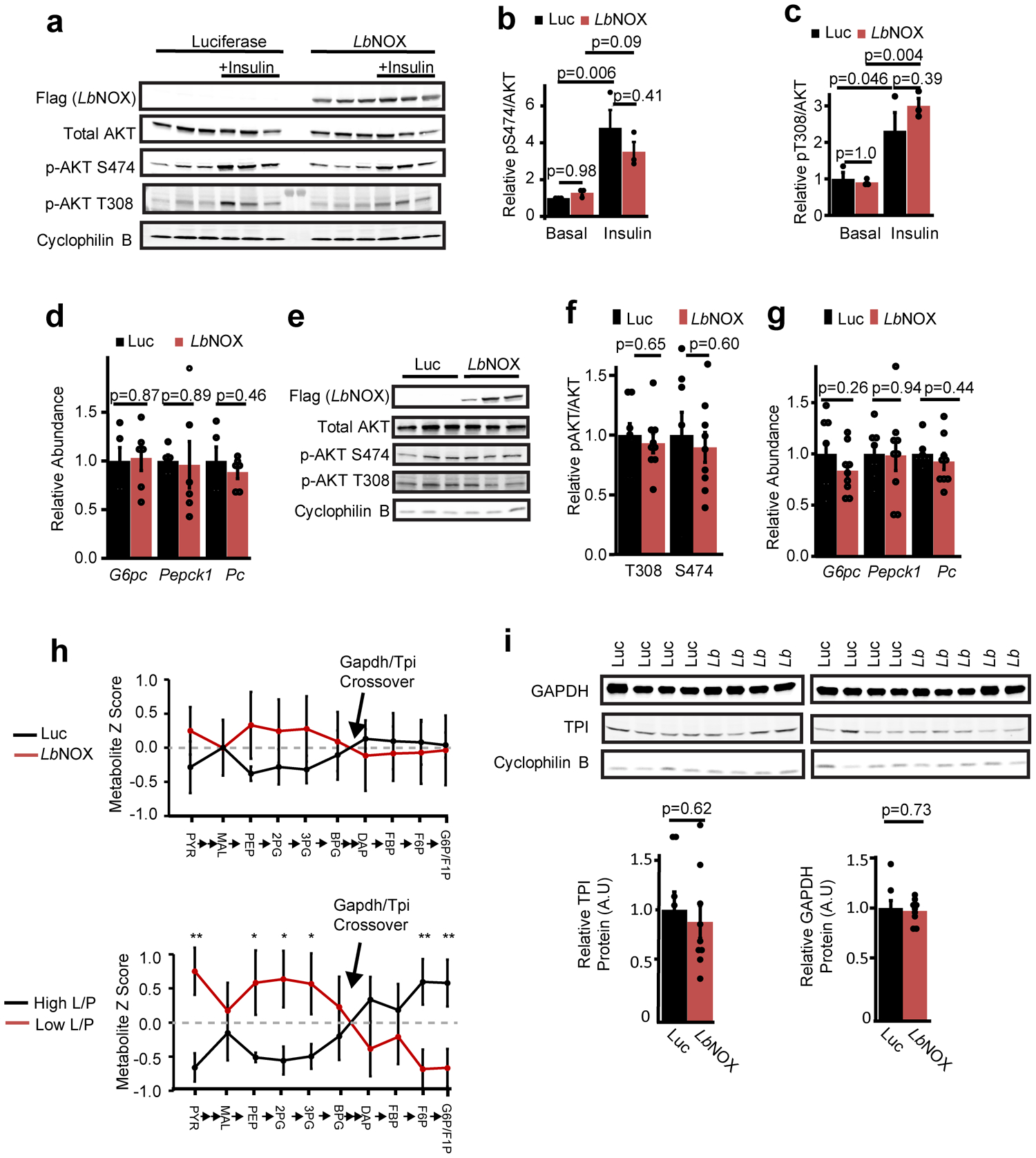
(a) Western blots of liver lysate from DIO mice 15 minutes after an i.p. injection of saline or 2 U/kg insulin with relative pS474 Akt/total Akt (b) and pT308 Akt/total Akt (c), n=3 from representative western from two independent experiments. (d) Transcriptional Foxo1 targets G6pc, Pepck1, and PC in DIO mice with LbNOX or luciferase, n=6. (e) Western blots of liver lysates at the end of hyperinsulinemic-eugylcemic clamps, n=3 representative of n=8 (Luciferase) and 9 (LbNOX) with (f) relative pS474 Akt/total Akt and pT308 Akt/total Akt (g) transcriptional Foxo1 targets G6pc, Pepck1, and Pc. n=8 (Luciferase), 9 (LbNOX). (h) Crossover analysis of relative abundance of gluconeogenic intermediates at end of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps. In the top panel, LbNOX vs. luciferase mice are compared. In the bottom panel, samples are divided by high or low liver lactate/pyruvate ratios and compared. (i) Relative protein levels of Gapdh and TPI at the end of the insulin clamp.n=8 (Luciferase), 9 (LbNOX). *, **, = p < 0.05, 0.01, using two-sided Student’s T test. Data are reported as mean±SEM.
