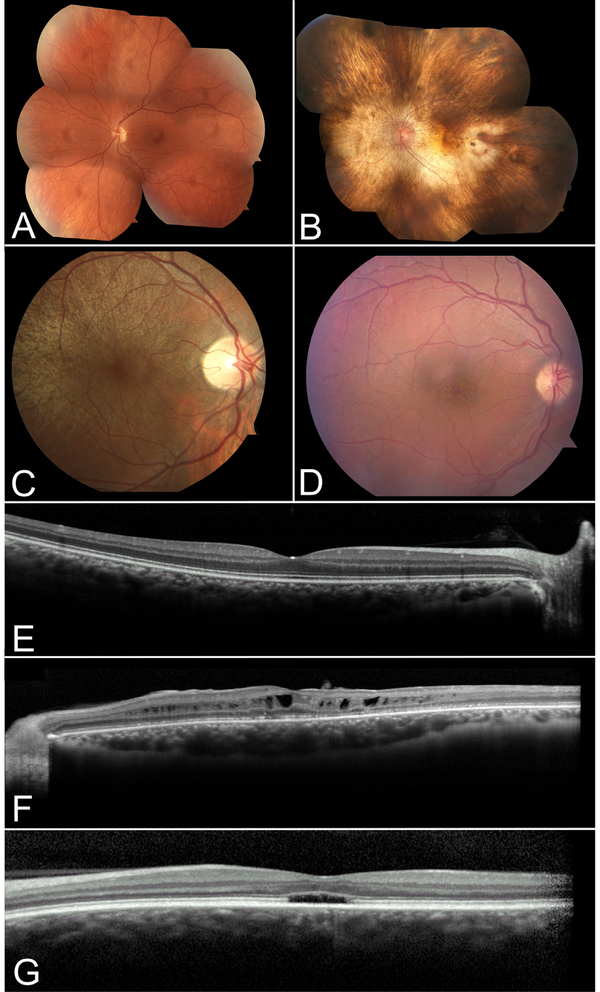
Figure 3. Retinal imaging of patients with inherited retinal disease.
Color fundoscopy of a normal patient (A) compared to patients with choroideremia (B), asymptomatic RPGR-associated RP female carrier (C) and retinoschisis (D). OCT of a normal patient depicting high resolution image of the retinal layers (E) compared to patients with retinoschisis (F) and achromatopsia (G). In B, note the characteristic pale fundus of choroideremia as a result of the sclera transilluminating through a degenerating RPE and choroid. In C, a typical tapetal-like reflex of the retina in an RPGR-associated RP carrier can be seen sparing the macula. In D, the subtle spoke-wheel appearance of retinoschisis is seen on color fundoscopy, and characteristic foveal and perifoveal cysts are seen on OCT in F. Patients with achromatopsia can show a foveal optical gap with loss of the inner and outer segment junction on OCT as depicted in G.